Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is essential for Hsp70-like protein 1 (HSP70L1) to activate dendritic cells and induce Th1 response
- PMID: 21730052
- PMCID: PMC3162398
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.266528
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is essential for Hsp70-like protein 1 (HSP70L1) to activate dendritic cells and induce Th1 response
Abstract
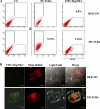
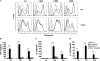
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play important roles in initiation of innate and adaptive immune responses. Emerging evidence suggests that TLR agonists can serve as potential adjuvant for vaccination. Heat shock proteins (HSPs), functionally serving as TLR4 agonists, have been proposed to act as Th1 adjuvant. We have identified a novel Hsp70 family member, termed Hsp70-like protein 1 (Hsp70L1), shown that Hsp70L1 is a potent T helper cell (Th1) polarizing adjuvant that contributes to antitumor immune responses. However, the underlying mechanism for how Hsp70L1 exerts its Th1 adjuvant activity remains to be elucidated. In this study, we found that Hsp70L1 binds directly to TLR4 on the surface of DCs, activates MAPK and NF-κB pathways, up-regulates I-a(b), CD40, CD80, and CD86 expression and promotes production of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-12p70. Hsp70L1 failed to induce such phenotypic maturation and cytokine production in TLR4-deficient DCs, indicating a role for TLR4 in mediating Hsp70L1-induced DC activation. Furthermore, more efficient induction of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-specific Th1 immune response was observed in mice immunized by wild-type DCs pulsed with Hsp70L1-CEA(576-669) fusion protein as compared with TLR4-deficient DCs pulsed with same fusion protein. In addition, TLR4 antagonist impaired induction of CEA-specific human Th1 immune response in a co-culture system of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) from HLA-A2.1(+) healthy donors and autologous DCs pulsed with Hsp70L1-CEA(576-669) in vitro. Taken together, these results demonstrate that TLR4 is a key receptor mediating the interaction of Hsp70L1 with DCs and subsequently enhancing the induction of Th1 immune response by Hsp70L1/antigen fusion protein.
Figures

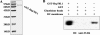
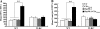
References
-
- Takeuchi O., Akira S. (2010) Cell 140, 805–820 - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. (2010) Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 - PubMed
-
- Lundberg A. M., Drexler S. K., Monaco C., Williams L. M., Sacre S. M., Feldmann M., Foxwell B. M. (2007) Blood 110, 3245–3252 - PubMed
-
- Peter M. E., Kubarenko A. V., Weber A. N., Dalpke A. H. (2009) J. Immunol. 182, 7690–7697 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

