Rerooting the evolutionary tree of malaria parasites
- PMID: 21730128
- PMCID: PMC3156215
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1109153108
Rerooting the evolutionary tree of malaria parasites
Abstract
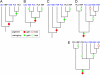
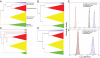
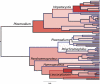
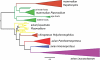
Malaria parasites (Plasmodium spp.) have plagued humans for millennia. Less well known are related parasites (Haemosporida), with diverse life cycles and dipteran vectors that infect other vertebrates. Understanding the evolution of parasite life histories, including switches between hosts and vectors, depends on knowledge of evolutionary relationships among parasite lineages. In particular, inferences concerning time of origin and trait evolution require correct placement of the root of the evolutionary tree. Phylogenetic reconstructions of the diversification of malaria parasites from DNA sequences have suffered from uncertainty concerning outgroup taxa, limited taxon sampling, and selection on genes used to assess relationships. As a result, inferred relationships among the Haemosporida have been unstable, and questions concerning evolutionary diversification and host switching remain unanswered. A recent phylogeny placed mammalian malaria parasites, as well as avian/reptilian Plasmodium, in a derived position relative to the avian parasite genera Leucocytozoon and Haemoproteus, implying that the ancestral forms lacked merogony in the blood and that their vectors were non-mosquito dipterans. Bayesian, outgroup-free phylogenetic reconstruction using relaxed molecular clocks with uncorrelated rates instead suggested that mammalian and avian/reptilian Plasmodium parasites, spread by mosquito vectors, are ancestral sister taxa, from which a variety of specialized parasite lineages with modified life histories have evolved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Resolving the phylogeny of malaria parasites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 9;108(32):12973-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1110141108. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21804030 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Garnham PCC. Malaria Parasites and Other Haemosporidia. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific; 1966.
-
- Valkiunas G. Avian Malaria Parasites and Other Haemosporidia. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2005.
-
- Chasar A, et al. Prevalence and diversity patterns of avian blood parasites in degraded African rainforest habitats. Mol Ecol. 2009;18:4121–4133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

