Targeting the regulation of androgen receptor signaling by the heat shock protein 90 cochaperone FKBP52 in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 21730179
- PMCID: PMC3141981
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1105160108
Targeting the regulation of androgen receptor signaling by the heat shock protein 90 cochaperone FKBP52 in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
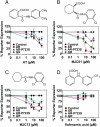
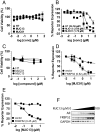
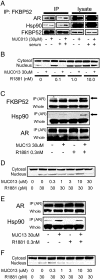
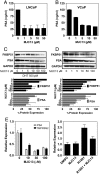
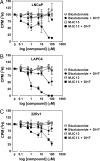
Drugs that target novel surfaces on the androgen receptor (AR) and/or novel AR regulatory mechanisms are promising alternatives for the treatment of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. The 52 kDa FK506 binding protein (FKBP52) is an important positive regulator of AR in cellular and whole animal models and represents an attractive target for the treatment of prostate cancer. We used a modified receptor-mediated reporter assay in yeast to screen a diversified natural compound library for inhibitors of FKBP52-enhanced AR function. The lead compound, termed MJC13, inhibits AR function by preventing hormone-dependent dissociation of the Hsp90-FKBP52-AR complex, which results in less hormone-bound receptor in the nucleus. Assays in early and late stage human prostate cancer cells demonstrated that MJC13 inhibits AR-dependent gene expression and androgen-stimulated prostate cancer cell proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: targeting the regulation of androgen receptor signaling by the heat shock protein 90 cochaperone FKBP52 in prostate cancer cells.J Urol. 2012 Mar;187(3):1128. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.11.023. Epub 2012 Jan 21. J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22325547 No abstract available.
-
Words of wisdom. Re: Targeting the regulation of androgen receptor signaling by the heat shock protein 90 cochaperone FKBP52 in prostate cancer cells.Eur Urol. 2012 Nov;62(5):931-2. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.08.040. Eur Urol. 2012. PMID: 23036345 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cheung-Flynn J, et al. Physiological role for the cochaperone FKBP52 in androgen receptor signaling. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19:1654–1666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

