Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 prevents early atherosclerosis by limiting lesional apoptosis and inflammatory Ly-6Chigh monocytosis: evidence that the effects are not apolipoprotein E dependent
- PMID: 21730304
- PMCID: PMC3144781
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.032268
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 prevents early atherosclerosis by limiting lesional apoptosis and inflammatory Ly-6Chigh monocytosis: evidence that the effects are not apolipoprotein E dependent
Abstract
Background: We previously demonstrated that macrophage low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR)-related protein 1 (LRP1) deficiency increases atherosclerosis despite antiatherogenic changes including decreased uptake of remnants and increased secretion of apolipoprotein E (apoE). Thus, our objective was to determine whether the atheroprotective effects of LRP1 require interaction with apoE, one of its ligands with multiple beneficial effects.
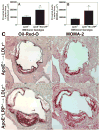
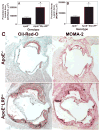
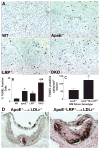
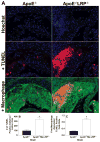
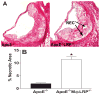
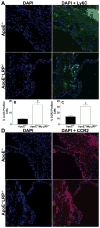
Methods and results: We examined atherosclerosis development in mice with specific deletion of macrophage LRP1 (apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-)) and in LDLR(-/-) mice reconstituted with apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) bone marrow. The combined absence of apoE and LRP1 promoted atherogenesis more than did macrophage apoE deletion alone in both apoE-producing LDLR(-/-) mice (+88%) and apoE(-/-) mice (+163%). The lesions of both mouse models with apoE(-/-) LRP1(-/-) macrophages had increased macrophage content. In vitro, apoE and LRP1 additively inhibit macrophage apoptosis. Furthermore, there was excessive accumulation of apoptotic cells in lesions of both LDLR(-/-) mice (+110%) and apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) mice (+252%). The apoptotic cell accumulation was partially due to decreased efferocytosis as the ratio of free to cell-associated apoptotic nuclei was 3.5-fold higher in lesions of apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) versus apoE(-/-) mice. Lesion necrosis was also increased (6 fold) in apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) versus apoE(-/-) mice. Compared with apoE(-/-) mice, the spleens of apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) mice contained 1.6- and 2.4-fold more total and Ly6-C(high) monocytes. Finally, there were 3.6- and 2.4-fold increases in Ly6-C(high) and CC-chemokine receptor 2-positive cells in lesions of apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) versus apoE(-/-) mice, suggesting that accumulation of apoptotic cells enhances lesion development and macrophage content by promoting the recruitment of inflammatory monocytes.
Conclusion: Low-density lipoprotein receptor protein 1 exerts antiatherogenic effects via pathways independent of apoE involving macrophage apoptosis and monocyte recruitment.
Figures
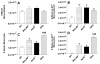
Similar articles
-
Loss of Macrophage Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 Confers Resistance to the Antiatherogenic Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibition.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Aug;36(8):1483-95. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307736. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27365402 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Macrophage Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1) Accelerates Atherosclerosis Regression and Increases C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 (CCR7) Expression in Plaque Macrophages.Circulation. 2018 Oct 23;138(17):1850-1863. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031702. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29794082 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-3/granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor promotes stem cell expansion, monocytosis, and atheroma macrophage burden in mice with hematopoietic ApoE deficiency.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 May;34(5):976-84. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.303097. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24651678 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 (AEBP1) (a novel macrophage proinflammatory mediator) overexpression promotes and ablation attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE (-/-) and LDLR (-/-) mice.Mol Med. 2011 Sep-Oct;17(9-10):1056-64. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00141. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21687917 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E regulation of myeloid cell plasticity in atherosclerosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012 Oct;23(5):471-8. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328356f967. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 22892903 Review.
Cited by
-
Living on the Edge: Efferocytosis at the Interface of Homeostasis and Pathology.Immunity. 2019 May 21;50(5):1149-1162. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.018. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 31117011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-155 deficiency results in decreased macrophage inflammation and attenuated atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Apr;34(4):759-67. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302701. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24504735 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating atherosclerosis: Integrating vaccines with gene targets.Am Heart J Plus. 2025 Aug 6;57:100588. doi: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2025.100588. eCollection 2025 Sep. Am Heart J Plus. 2025. PMID: 40823653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and Consequences of Defective Efferocytosis in Atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Jan 8;4:86. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00086. eCollection 2017. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29379788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel.Eur Heart J. 2020 Jun 21;41(24):2313-2330. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz962. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32052833 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Linton MF, Atkinson JB, Fazio S. Prevention of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by bone marrow transplantation. Science. 1995;267:1034–1037. - PubMed
-
- Fazio S, Babaev V, Burleigh M, Major A, Hasty A, Linton M. Physiologic expression of macrophage apoE in the artery wall reduces atherosclerosis in severely hyperlipidemic mice. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:1602–1609. - PubMed
-
- Overton CD, Yancey PG, Major AS, Linton MF, Fazio S. Deletion of Macrophage LDL Receptor-Related Protein Increases Atherogenesis in the Mouse. Circ Res. 2007;100:670–677. - PubMed
-
- Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988;240:622–630. - PubMed
-
- Williams DL, Dawson PA, Newman TC, Rudel LL. Apolipoprotein E synthesis in peripheral tissues of nonhuman primates. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:2444–2451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

