Necrotizing enterocolitis in the premature infant: neonatal nursing assessment, disease pathogenesis, and clinical presentation
- PMID: 21730907
- PMCID: PMC3759524
- DOI: 10.1097/ANC.0b013e31821baaf4
Necrotizing enterocolitis in the premature infant: neonatal nursing assessment, disease pathogenesis, and clinical presentation
Abstract
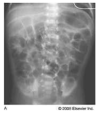
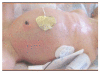
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) remains one of the most catastrophic comorbidities associated with prematurity. In spite of extensive research, the disease remains unsolved. The aims of this article are to present the current state of the science on the pathogenesis of NEC, summarize the clinical presentation and severity staging of the disease, and highlight the nursing assessments required for early identification of NEC and ongoing care for infants diagnosed with this gastrointestinal disease. The distributions of systemic and intestinal clinical signs that are most sensitive to nursing assessment and associated with Bell Staging Criteria are presented. These descriptive data are representative of 117 cases of NEC diagnosed in low-gestational-age infants (<29 weeks' gestation). The data highlight the clinical signs most commonly observed in infants with NEC and thus provide NICU nurses an evidence-based guide for assessment and care of infants with NEC.
Figures
References
-
- Henry MCW, Moss RL. Necrotizing enterocolitis. Ann Rev Med. 2009;60:111–24. - PubMed
-
- Moss RL, Kalish LA, Duggan C, et al. Clinical parameters do not adequately predict outcome in necrotizing enterocolitis: a multi-institutional study. J Perinatol. 2008;28(10):665–674. - PubMed
-
- Llanos AR, Moss ME, Pinzon MC, et al. Epidemiology of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: a population based study. Paediatr Perin Epidemiol. 2002;16:342–349. - PubMed
-
- Chandler JC, Hebra A. Necrotizing enterocolitis in infants with very low birth weight. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2000;9:63–72. - PubMed
-
- Petty JK, Ziegler MM. Operative strategies for necrotizing enterocolitis: the prevention and treatment of short-bowel syndrome. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2005;14:191–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

