Sch9 regulates ribosome biogenesis via Stb3, Dot6 and Tod6 and the histone deacetylase complex RPD3L
- PMID: 21730963
- PMCID: PMC3160192
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.221
Sch9 regulates ribosome biogenesis via Stb3, Dot6 and Tod6 and the histone deacetylase complex RPD3L
Abstract
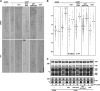
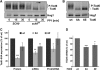
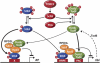
TORC1 is a conserved multisubunit kinase complex that regulates many aspects of eukaryotic growth including the biosynthesis of ribosomes. The TOR protein kinase resident in TORC1 is responsive to environmental cues and is potently inhibited by the natural product rapamycin. Recent characterization of the rapamycin-sensitive phosphoproteome in yeast has yielded insights into how TORC1 regulates growth. Here, we show that Sch9, an AGC family kinase and direct substrate of TORC1, promotes ribosome biogenesis (Ribi) and ribosomal protein (RP) gene expression via direct inhibitory phosphorylation of the transcriptional repressors Stb3, Dot6 and Tod6. Deletion of STB3, DOT6 and TOD6 partially bypasses the growth and cell size defects of an sch9 strain and reveals interdependent regulation of both Ribi and RP gene expression, and other aspects of Ribi. Dephosphorylation of Stb3, Dot6 and Tod6 enables recruitment of the RPD3L histone deacetylase complex to repress Ribi/RP gene promoters. Taken together with previous studies, these results suggest that Sch9 is a master regulator of ribosome biogenesis through the control of Ribi, RP, ribosomal RNA and tRNA gene transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magalhaes PJ, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton Int 11: 36–41
-
- Badis G, Chan ET, van Bakel H, Pena-Castillo L, Tillo D, Tsui K, Carlson CD, Gossett AJ, Hasinoff MJ, Warren CL, Gebbia M, Talukder S, Yang A, Mnaimneh S, Terterov D, Coburn D, Li Yeo A, Yeo ZX, Clarke ND, Lieb JD et al. (2008) A library of yeast transcription factor motifs reveals a widespread function for Rsc3 in targeting nucleosome exclusion at promoters. Mol Cell 32: 878–887 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bianchi A, Negrini S, Shore D (2004) Delivery of yeast telomerase to a DNA break depends on the recruitment functions of Cdc13 and Est1. Mol Cell 16: 139–146 - PubMed
-
- Breitkreutz A, Choi H, Sharom JR, Boucher L, Neduva V, Larsen B, Lin ZY, Breitkreutz BJ, Stark C, Liu G, Ahn J, Dewar-Darch D, Reguly T, Tang X, Almeida R, Qin ZS, Pawson T, Gingras AC, Nesvizhskii AI, Tyers M (2010) A global protein kinase and phosphatase interaction network in yeast. Science 328: 1043–1046 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

