Odontoameloblastoma
- PMID: 21731280
- PMCID: PMC3125659
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.80028
Odontoameloblastoma
Abstract
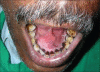
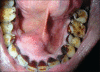
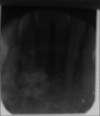
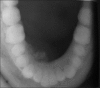
Odontoameloblastoma (OA) is an extremely rare mixed odontogenic tumor with both epithelial and mesenchymal components. OA develops from proliferating odontogenic epithelium and mesenchymal tissue. Till date, around 20 cases have fulfilled the histologic criteria of the current World Health Organization (WHO) histologic classification of odontogenic tumors. It affects predominantly young patients with a median age of 20.12 years, and has a predilection for males and occurs in posterior segments of either jaw with slight inclination for mandible. Review of literature shows only three reported cases in the anterior mandible. Here, we report a case of OA in the anterior mandible.
Keywords: Odontoameloblastoma; ameloblasic dentinoma; mixed odontogenic tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Reichart PA, Philipsen HP. Odontogenic Tumors and Allied Lesions. Chicago: Quintessence Publication; 2004. pp. 171–3.
-
- Thompson IO, Phillips VM, Ferreira R, Housego TG. Odontoameloblastoma: A case report. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990;28:347–9. - PubMed
-
- Mosqueda-Taylor A, Carlos-Bregni R, Ramírez-Amador V, Palma-Guzmán JM, Esquivel-Bonilla D, Hernández-Rojase LA. Odontoameloblastoma. Clinicopathologic study of 3 cases and critical review of literature. Oral Oncol. 2002;38:800–5. - PubMed
-
- Martín-Granizo-López R, López-García-Asenjo J, de-Pedro-Marina M, Domínguez-Cuadrado L. Odontoameloblastoma: A Case Report and A Review of Literature. Med Oral. 2004;9:340–4. - PubMed
-
- Gupta DS, Gupta MK. Odontoameloblastoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986;44:146–8. - PubMed

