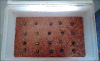
Effect of methanolic extract of Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) Standley fruits on marble-burying behavior in mice: Implications for obsessive-compulsive disorder
- PMID: 21731398
- PMCID: PMC3119274
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-8490.79118
Effect of methanolic extract of Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) Standley fruits on marble-burying behavior in mice: Implications for obsessive-compulsive disorder
Abstract
Context: Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is the fourth most common mental disorder and is diagnosed nearly as often as asthma and diabetes mellitus. Over the last decade, the inhibition of burying of glass marbles by mice has been used as an index of anti-OCD drug action in the so-called marble-burying test. Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) Standley (LS), commonly known as "bottle gourd" (English), possesses several medicinal properties; little is known about its action as a nerve tonic.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to characterize the anti-OCD (anti-compulsive) activity of the methanolic extract of the fruits of L. siceraria (Molina) Standley (LS) using the marble-burying behavior in mice.
Materials and methods: The experiment was conducted in specific animal models of Swiss albino mice to evaluate marble-burying behavior.
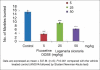
Results and conclusions: Intraperitonial administration of 25 and 50 mg/kg of LS extract significantly (P < 0.001) decreased the total number of buried marbles. The effect was comparable to that of the fluoxetine (10 mg/kg, i.p.). Fluoxetine and LS fruit extract do not produce any overt motor dysfunction. Preliminary phytochemical screening of the methanolic extract of LS showed the presence of flavonoids, saponins, sterols, proteins, tannins and carbohydrates. The results of the study for the first time show that the plant possesses anti-compulsive (anti-OCD) activity, confirming the traditional claims. Future research should focus on the identification and the mechanism of action of the constituents from this plant.
Keywords: Fluoxetine; Lagenaria siceraria; marble-burying behavior; obsessive–compulsive disorder; preliminary phytochemical screening.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rasmussen SA, Eisen JL. The epidemiology and clinical features of obsessive- compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1992;15:743–58. - PubMed
-
- Bartz JA, Hollander E. Is obsessive-compulsive disorder an anxiety disorder? Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006;30:338–52. - PubMed
-
- El Mansari M, Blier P. Mechanisms of action of current and potential pharmacotherapies of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006;30:362–73. - PubMed
-
- Joel D. Current animal models of obsessive-compulsive disorder: A critical review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006;30:374–88. - PubMed
-
- Archer T, Fredriksson A, Lewander T, Soderberg U. Marble burying and spontaneous motor activity in mice: Interactions over days and the effect of diazepam. Scand Psychol. 1987;28:242–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources