Improving the accuracy of Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculation for homolysis bond dissociation energies of Y-NO bond: generalized regression neural network based on grey relational analysis and principal component analysis
- PMID: 21731439
- PMCID: PMC3127115
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12042242
Improving the accuracy of Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculation for homolysis bond dissociation energies of Y-NO bond: generalized regression neural network based on grey relational analysis and principal component analysis
Abstract
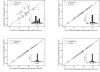
We propose a generalized regression neural network (GRNN) approach based on grey relational analysis (GRA) and principal component analysis (PCA) (GP-GRNN) to improve the accuracy of density functional theory (DFT) calculation for homolysis bond dissociation energies (BDE) of Y-NO bond. As a demonstration, this combined quantum chemistry calculation with the GP-GRNN approach has been applied to evaluate the homolysis BDE of 92 Y-NO organic molecules. The results show that the ull-descriptor GRNN without GRA and PCA (F-GRNN) and with GRA (G-GRNN) approaches reduce the root-mean-square (RMS) of the calculated homolysis BDE of 92 organic molecules from 5.31 to 0.49 and 0.39 kcal mol(-1) for the B3LYP/6-31G (d) calculation. Then the newly developed GP-GRNN approach further reduces the RMS to 0.31 kcal mol(-1). Thus, the GP-GRNN correction on top of B3LYP/6-31G (d) can improve the accuracy of calculating the homolysis BDE in quantum chemistry and can predict homolysis BDE which cannot be obtained experimentally.
Keywords: Y-NO bond; density functional theory; generalized regression neural network; grey relational analysis; homolysis bond dissociation energy; principal component analysis.
Figures


References
-
- Butler AR, Williams DLH. The physiological role of nitric oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1993;22:233–241.
-
- Averill BA. Dissimilatory nitrite and nitric oxide reductases. Chem. Rev. 1996;96:2951–2964. - PubMed
-
- Palmer RMJ, Ferrige AG, Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987;327:524–526. - PubMed
-
- Ignarro LJ. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. - PubMed
-
- Feldman PL, Griffith OW, Stuehr DJ. The surprising life of nitric oxide. Chem. Eng. News. 1993;71:26–38.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

