T regulatory cells are markers of disease activity in multiple sclerosis patients
- PMID: 21731726
- PMCID: PMC3123332
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021386
T regulatory cells are markers of disease activity in multiple sclerosis patients
Abstract
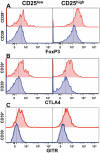
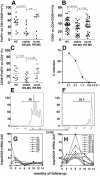
FoxP3⁺ Treg cells are believed to play a role in the occurrence of autoimmunity and in the determination of clinical recurrences. Contradictory reports are, however, available describing frequency and function of Treg cells during autoimmune diseases. We examined, by both polychromatic flow cytometry, and real-time RT-PCR, several Treg markers in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system. We found that Tregs, as defined by CD25, CD39, FoxP3, CTLA4, and GITR expression, were significantly decreased in stable MS patients as compared to healthy donors, but, surprisingly, restored to normal levels during an acute clinical attack. We conclude that Treg cells are not involved in causing clinical relapses, but rather react to inflammation in the attempt to restore homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Kasper LH, Haque A, Haque S. Regulatory mechanisms of the immune system in multiple sclerosis. T regulatory cells: turned on to turn off. J Neurol. 2007;254(Suppl 1):I10–I14.
-
- Kohm AP, Carpentier PA, Anger HA, Miller SD. Cutting edge: CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress antigen-specific autoreactive immune responses and central nervous system inflammation during active experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2002;169:4712–4716. - PubMed
-
- Huan J, Culbertson N, Spencer L, Bartholomew R, Burrows GG, et al. Decreased FOXP3 levels in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurosci Res. 2005;81:45–52. - PubMed
-
- Putheti P, Pettersson A, Soderstrom M, Link H, Huang YM. Circulating CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells are not altered in multiple sclerosis and unaffected by disease-modulating drugs. J Clin Immunol. 2004;24:155–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

