Deletion of Ia-2 and/or Ia-2β in mice decreases insulin secretion by reducing the number of dense core vesicles
- PMID: 21732083
- PMCID: PMC3168514
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-011-2221-6
Deletion of Ia-2 and/or Ia-2β in mice decreases insulin secretion by reducing the number of dense core vesicles
Abstract
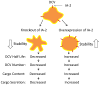
Aims/hypothesis: Islet antigen 2 (IA-2) and IA-2β are dense core vesicle (DCV) transmembrane proteins and major autoantigens in type 1 diabetes. The present experiments were initiated to test the hypothesis that the knockout of the genes encoding these proteins impairs the secretion of insulin by reducing the number of DCV.
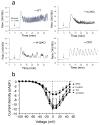
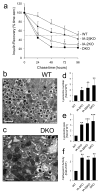
Methods: Insulin secretion, content and DCV number were evaluated in islets from single knockout (Ia-2 [also known as Ptprn] KO, Ia-2β [also known as Ptprn2] KO) and double knockout (DKO) mice by a variety of techniques including electron and two-photon microscopy, membrane capacitance, Ca(2+) currents, DCV half-life, lysosome number and size and autophagy.
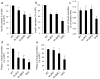
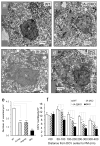
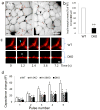
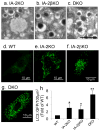
Results: Islets from single and DKO mice all showed a significant decrease in insulin content, insulin secretion and the number and half-life of DCV (p < 0.05 to 0.001). Exocytosis as evaluated by two-photon microscopy, membrane capacitance and Ca(2+) currents supports these findings. Electron microscopy of islets from KO mice revealed a marked increase (p < 0.05 to 0.001) in the number and size of lysosomes and enzymatic studies showed an increase in cathepsin D activity (p < 0.01). LC3 protein, an indicator of autophagy, also was increased in islets of KO compared with wild-type mice (p < 0.05 to 0.01) suggesting that autophagy might be involved in the deletion of DCV.
Conclusions/interpretation: We conclude that the decrease in insulin content and secretion, resulting from the deletion of Ia-2 and/or Ia-2β, is due to a decrease in the number of DCV.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Lan MS, Lu J, Goto Y, Notkins AL. Molecular cloning and identification of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, IA-2, from human insulinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 1994;13:505–514. - PubMed
-
- Verge CF, Gianani R, Kawasaki E, et al. Prediction of type I diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, and ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies. Diabetes. 1996;45:926–933. - PubMed
-
- Bingley PJ, Bonifacio E, Gale EA. Can we really predict IDDM? Diabetes. 1993;42:213–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

