Rspo2/Int7 regulates invasiveness and tumorigenic properties of mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 21732367
- PMCID: PMC6957254
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.22924
Rspo2/Int7 regulates invasiveness and tumorigenic properties of mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
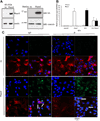
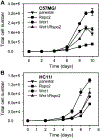
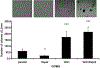
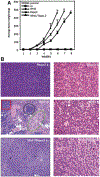
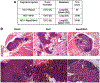
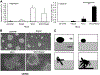
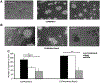
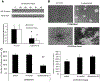
Rspo2 was identified as a novel common integration site (CIS) for the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) in viral induced mouse mammary tumors. Here we show that Rspo2 modulates Wnt signaling in mouse mammary epithelial cells. Co-expression of both genes resulted in an intermediate growth phenotype on plastic and had minor effects on the growth-promoting properties of Wnt1 in soft agar. However, individual Rspo2 and Wnt1 HC11 transfectants as well as the double transfectant were tumorigenic in athymic nude mice, with tumors from each line having distinctive histological characteristics. Rspo2 and Rspo2/Wnt1 tumors contained many spindle cells, consistent with an epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) phenotype. When Rspo2 and Rspo2/Wnt1 tumor cells were transferred into naïve mice, they exhibited greater metastatic activity than cells derived from Wnt1 tumors. For comparison, C57MG/Wnt1/Rspo2 co-transfectants exhibited invasive properties in three-dimensional (3D) Matrigel cultures that were not seen with cells transfected only with Wnt1 or Rspo2. Use of Dickkopf-1, a specific antagonist of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, or short hairpin RNA targeting β-catenin expression demonstrated that the invasive activity was not mediated by β-catenin. Our results indicate that Rspo2 and Wnt1 have mutually distinct effects on mammary epithelial cell growth and these effects are context-dependent. While Rspo2 and Wnt1 act synergistically in the β-catenin pathway, other mechanisms are responsible for the invasive properties of stable double transfectants observed in 3D Matrigel cultures.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Bafico A, Gazit A, Wu-Morgan SS, Yaniv A, Aaronson SA. 1998. Characterization of Wnt-1 and Wnt-2 induced growth alterations and signaling pathways in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Oncogene 16:2819–2825. - PubMed
-
- Bejsovec A 2005. Wnt pathway activation: New relations and locations. Cell 120:11–14. - PubMed
-
- Binnerts ME, Kim KA, Bright JM, Patel SM, Tran K, Zhou M, Leung JM, Liu Y, Lomas WE III, Dixon M, Hazell SA, Wagle M, Nie WS, Tomasevic N, Williams J, Zhan X, Levy MD, Funk WD, Abo A. 2007. R-Spondin1 regulates Wnt signaling by inhibiting internalization of LRP6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14700–14705. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cadigan KM, Liu YI. 2006. Wnt signaling: Complexity at the surface. J Cell Sci 119:395–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

