Impulsivity and cognitive distortions in pathological gamblers attending the UK National Problem Gambling Clinic: a preliminary report
- PMID: 21733207
- PMCID: PMC3206226
- DOI: 10.1017/S003329171100095X
Impulsivity and cognitive distortions in pathological gamblers attending the UK National Problem Gambling Clinic: a preliminary report
Abstract
Background: Pathological gambling (PG) is a form of behavioural addiction that has been associated with elevated impulsivity and also cognitive distortions in the processing of chance, probability and skill. We sought to assess the relationship between the level of cognitive distortions and state and trait measures of impulsivity in treatment-seeking pathological gamblers.
Method: Thirty pathological gamblers attending the National Problem Gambling Clinic, the first National Health Service clinic for gambling problems in the UK, were compared with 30 healthy controls in a case-control design. Cognitive distortions were assessed using the Gambling-Related Cognitions Scale (GRCS). Trait impulsivity was assessed using the UPPS-P, which includes scales of urgency, the tendency to be impulsive in positive or negative mood states. Delay discounting rates were taken as a state measure of impulsive choice.
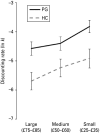
Results: Pathological gamblers had elevated impulsivity on several UPPS-P subscales but effect sizes were largest (Cohen's d>1.4) for positive and negative urgency. The pathological gamblers also displayed higher levels of gambling distortions, and elevated preference for immediate rewards, compared to controls. Within the pathological gamblers, there was a strong relationship between the preference for immediate rewards and the level of cognitive distortions (R2=0.41).
Conclusions: Impulsive choice in the gamblers was correlated with the level of gambling distortions, and we hypothesize that an impulsive decision-making style may increase the acceptance of erroneous beliefs during gambling play.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impulsivity and Gambling Type Among Treatment-Seeking Disordered Gamblers: An Explorative Study.J Gambl Stud. 2018 Dec;34(4):1341-1354. doi: 10.1007/s10899-018-9764-0. J Gambl Stud. 2018. PMID: 29502327
-
Impulsivity and cognitive distortions in different clinical phenotypes of gambling disorder: Profiles and longitudinal prediction of treatment outcomes.Eur Psychiatry. 2019 Sep;61:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Eur Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31255958
-
Impulsive action but not impulsive choice determines problem gambling severity.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050647. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209796 Free PMC article.
-
[To an integrative management of pathological gamblers].Encephale. 2011 Dec;37(6):410-7. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Encephale. 2011. PMID: 22137212 Review. French.
-
Pathological gambling: an impulse control disorder? Measurement of impulsivity using neurocognitive tests.Isr Med Assoc J. 2010 Apr;12(4):243-8. Isr Med Assoc J. 2010. PMID: 20803888 Review.
Cited by
-
Irrational choice under uncertainty correlates with lower striatal D(2/3) receptor binding in rats.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 31;32(44):15450-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0626-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23115182 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Problem Gambling Severity: Interplay between Emotion Dysregulation and Gambling-related Cognitions.J Gambl Stud. 2022 Jun;38(2):483-498. doi: 10.1007/s10899-021-10039-w. Epub 2021 May 31. J Gambl Stud. 2022. PMID: 34057668
-
Risk Factors for Gambling Problems Specifically Associated with Sports Betting.J Gambl Stud. 2019 Dec;35(4):1211-1228. doi: 10.1007/s10899-019-09848-x. J Gambl Stud. 2019. PMID: 30924002
-
Impulsivity and Gambling Type Among Treatment-Seeking Disordered Gamblers: An Explorative Study.J Gambl Stud. 2018 Dec;34(4):1341-1354. doi: 10.1007/s10899-018-9764-0. J Gambl Stud. 2018. PMID: 29502327
-
Internet Gamblers Differ on Social Variables: A Latent Class Analysis.J Gambl Stud. 2017 Sep;33(3):881-897. doi: 10.1007/s10899-016-9664-0. J Gambl Stud. 2017. PMID: 28028687
References
-
- Alessi SM, Petry NM. Pathological gambling severity is associated with impulsivity in a delay discounting procedure. Behavioral Processes. 2003;64:345–354. - PubMed
-
- Anderson G, Brown RI. Real and laboratory gambling, sensation-seeking and arousal. British Journal of Psychology. 1984;75:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Anestis MD, Selby EA, Fink EL, Joiner TE. The multifaceted role of distress tolerance in dysregulated eating behaviors. International Journal of Eating Disorders. 2007;40:718–726. - PubMed
-
- Bickel WK, Marsch LA. Toward a behavioral economic understanding of drug dependence: delay discounting processes. Addiction. 2001;96:73–86. - PubMed
-
- Billieux J, Gay P, Rochat L, Van Der Linden M. The role of urgency and its underlying psychological mechanisms in problematic behaviours. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2010;48:1085–1096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

