Lamotrigine blocks NMDA receptor-initiated arachidonic acid signalling in rat brain: implications for its efficacy in bipolar disorder
- PMID: 21733229
- PMCID: PMC3204186
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145711001003
Lamotrigine blocks NMDA receptor-initiated arachidonic acid signalling in rat brain: implications for its efficacy in bipolar disorder
Abstract
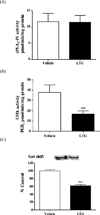
An up-regulated brain arachidonic acid (AA) cascade and a hyperglutamatergic state characterize bipolar disorder (BD). Lamotrigine (LTG), a mood stabilizer approved for treating BD, is reported to interfere with glutamatergic neurotransmission involving N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). NMDARs allow extracellular calcium into the cell, thereby stimulating calcium-dependent cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) to release AA from membrane phospholipid. We hypothesized that LTG, like other approved mood stabilizers, would reduce NMDAR-mediated AA signalling in rat brain. An acute subconvulsant dose of NMDA (25 mg/kg) or saline was administered intraperitoneally to unanaesthetized rats that had been treated p.o. daily for 42 d with vehicle or a therapeutically relevant dose of LTG (10 mg/kg.d). Regional brain AA incorporation coefficients k* and rates J in, and AA signals, were measured using quantitative autoradiography after intravenous [1-14C]AA infusion, as were other AA cascade markers. In chronic vehicle-treated rats, acute NMDA compared to saline increased k* and J in in widespread regions of the brain, as well as prostaglandin (PG)E2 and thromboxane B2 concentrations. Chronic LTG treatment compared to vehicle reduced brain cyclooxygenase (COX) activity, PGE2 concentration, and DNA-binding activity of the COX-2 transcription factor, NF-κB. Pretreatment with chronic LTG blocked the acute NMDA effects on AA cascade markers. In summary, chronic LTG like other mood stabilizers blocks NMDA-mediated signalling involving the AA metabolic cascade. Since markers of the AA cascade and of NMDAR signalling are up-regulated in the post-mortem BD brain, mood stabilizers generally may be effective in BD by dampening NMDAR signalling and the AA cascade.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic valproate treatment blocks D2-like receptor-mediated brain signaling via arachidonic acid in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Dec;61(8):1256-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.025. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21839100 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium and the other mood stabilizers effective in bipolar disorder target the rat brain arachidonic acid cascade.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Jun 18;5(6):459-67. doi: 10.1021/cn500058v. Epub 2014 May 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24786695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic administration of valproic acid reduces brain NMDA signaling via arachidonic acid in unanesthetized rats.Neurochem Res. 2008 Nov;33(11):2229-40. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9700-2. Epub 2008 May 7. Neurochem Res. 2008. PMID: 18461450 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic carbamazepine administration reduces N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-initiated signaling via arachidonic acid in rat brain.Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Oct 15;62(8):934-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.04.021. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17628508 Free PMC article.
-
Mood-stabilizers target the brain arachidonic acid cascade.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;2(2):207-14. doi: 10.2174/1874467210902020207. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20021459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Individuals with Bipolar Disorder Have a Higher Level of Homocysteine Than Major Depressive Disorder: A Retrospective Chart Review and Observational Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Nov 15;18:2671-2682. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S387063. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 36411779 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic valproate treatment blocks D2-like receptor-mediated brain signaling via arachidonic acid in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Dec;61(8):1256-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.025. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21839100 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaco-psychiatry and gut microbiome: a systematic review of effects of psychotropic drugs for bipolar disorder.Microbiology (Reading). 2025 Jun;171(6):001568. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001568. Microbiology (Reading). 2025. PMID: 40528728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined cell grafting and VPA administration facilitates neural repair through axonal regeneration and synaptogenesis in traumatic brain injury.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Sep 25;54(9):1289-1300. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022123. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 36148950 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium and the other mood stabilizers effective in bipolar disorder target the rat brain arachidonic acid cascade.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Jun 18;5(6):459-67. doi: 10.1021/cn500058v. Epub 2014 May 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24786695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad S, Fowler LJ, Whitton PS. Effects of acute and chronic lamotrigine treatment on basal and stimulated extracellular amino acids in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. Brain Research. 2004;1029:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Anand A, Charney DS, Oren DA, Berman RM, et al. Attenuation of the neuropsychiatric effects of ketamine with lamotrigine: support for hyperglutamatergic effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. Archives General Psychiatry. 2000;57:270–276. - PubMed
-
- Bacher A, Zornow MH. Lamotrigine inhibits extracellular glutamate accumulation during transient global cerebral ischemia in rabbits. Anesthesiology. 1997;86:459–463. - PubMed
-
- Bakare A, Shao L, Cui J, Young LT, et al. Mood stabilizing drugs lamotrigine and olanzapine increase expression and activity of glutathione S-transferase in primary cultured rat cerebral cortical cells. Neuroscience Letters. 2009;455:70–73. - PubMed
-
- Basselin M, Chang L, Bell JM, Rapoport SI. Chronic lithium chloride administration attenuates brain NMDA receptor-initiated signaling via arachidonic acid in unanesthetized rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006a;31:1659–1674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

