MKP-1 regulates cytokine mRNA stability through selectively modulation subcellular translocation of AUF1
- PMID: 21733716
- PMCID: PMC3185122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.06.006
MKP-1 regulates cytokine mRNA stability through selectively modulation subcellular translocation of AUF1
Abstract
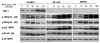
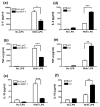
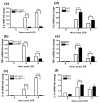
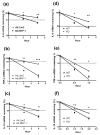
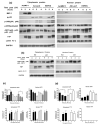
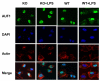
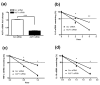
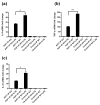
MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1)/dual specificity protein phosphatase-1 (DUSP-1) is a negative regulator of the host inflammatory response to infection. However, the mechanisms underlying the regulation of cytokine expression by MKP-1, especially at the post-transcriptional level, have not been fully delineated. In the current study, MKP-1 specifically dephosphorylated activated MAPK responses and attenuated LPS-induced IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α expression. In addition, MKP-1 was important in destabilizing cytokine mRNAs. In LPS-stimulated rat macrophages with overexpressed MKP-1, half-lives of IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α mRNAs were significantly reduced compared to controls. Conversely, half-lives of IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α mRNAs were significantly increased in bone marrow macrophages derived from MKP-1 knock out (KO) mice compared with macrophages derived from MKP-1 wild type (WT) mice. Furthermore, MKP-1 promoted translocation of RNA-binding protein (RNA-BP) ARE/poly-(U) binding degradation factor 1 (AUF1) from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to LPS stimulation as evidenced by Western blot and immunofluorescent staining. Knockdown AUF1 mRNA expression by AUF1 siRNA in MKP-1 WT bone marrow macrophages significantly delayed degradation of IL-6, IL-10 and TNF- α mRNAs compared with controls. Finally, AUF1 was immunoprecipitated with the RNA complex in cellular lysates derived from bone marrow macrophages of MKP-1 KO vs. WT mice, which had increased AUF1-bound target mRNAs, including IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α in WT macrophages compared with MKP-1 KO macrophages. Thus, this work provides new mechanistic insight of MKP-1 signaling and regulation of cytokine mRNA stability through RNA binding proteins in response to inflammatory stimuli.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel AU-rich-element-binding protein which is related to AUF1.Biochem J. 2002 Sep 15;366(Pt 3):709-19. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020402. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12086581 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of MAPK phosphatase-1 local gene transfer in inflammatory bone loss.Gene Ther. 2011 Apr;18(4):344-53. doi: 10.1038/gt.2010.139. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 21068780 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding protein AUF1 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced IL10 expression by activating IkappaB kinase complex in monocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;31(4):602-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00835-10. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21135123 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of neoplastic gene regulatory pathways by the RNA-binding factor AUF1.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jun 1;16(6):2307-25. doi: 10.2741/3855. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21622178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological networks and disease functions of RNA-binding protein AUF1.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Jul-Aug;5(4):549-64. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1230. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24687816 Review.
Cited by
-
Critical role of MKP-1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast formation through CXCL1 and CXCL2.Cytokine. 2015 Jan;71(1):71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Sep 27. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25261746 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Mitogen Kinase Phosphatase 1: A Critical Interplay in Macrophage Biology.Front Mol Biosci. 2016 Jun 28;3:28. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00028. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27446931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of TNFα production after heat and endotoxin stimulation is dependent on Annexin-A1 and HSP70.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015 Jul;20(4):583-93. doi: 10.1007/s12192-015-0580-5. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015. PMID: 25753354 Free PMC article.
-
MKP-1 signaling events are required for early osteoclastogenesis in lineage defined progenitor populations by disrupting RANKL-induced NFATc1 nuclear translocation.Bone. 2014 Mar;60:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.11.012. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Bone. 2014. PMID: 24269279 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and specificity of the mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 functions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jan;70(2):223-37. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1041-2. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22695679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang SH, Sharrocks AD, Whitmarsh AJ. Transcriptional regulation by the MAP kinase signaling cascades. Gene. 2003;320:3–21. - PubMed
-
- Whitmarsh AJ. Regulation of gene transcription by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:1285–98. Epub 2006 Nov 17. - PubMed
-
- Keyse SM. Protein phosphatases and the regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12:186–92. - PubMed
-
- Rincon M, Davis RJ. Regulation of the immune response by stress-activated protein kinases. Immunol Rev. 2009;228:212–24. - PubMed
-
- Slifka MK, Whitton JL. Clinical implications of dysregulated cytokine production. J Mol Med. 2000;78:74–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

