Mutation of the conserved polyadenosine RNA binding protein, ZC3H14/dNab2, impairs neural function in Drosophila and humans
- PMID: 21734151
- PMCID: PMC3145741
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1107103108
Mutation of the conserved polyadenosine RNA binding protein, ZC3H14/dNab2, impairs neural function in Drosophila and humans
Abstract
Here we report a human intellectual disability disease locus on chromosome 14q31.3 corresponding to mutation of the ZC3H14 gene that encodes a conserved polyadenosine RNA binding protein. We identify ZC3H14 mRNA transcripts in the human central nervous system, and we find that rodent ZC3H14 protein is expressed in hippocampal neurons and colocalizes with poly(A) RNA in neuronal cell bodies. A Drosophila melanogaster model of this disease created by mutation of the gene encoding the ZC3H14 ortholog dNab2, which also binds polyadenosine RNA, reveals that dNab2 is essential for development and required in neurons for normal locomotion and flight. Biochemical and genetic data indicate that dNab2 restricts bulk poly(A) tail length in vivo, suggesting that this function may underlie its role in development and disease. These studies reveal a conserved requirement for ZC3H14/dNab2 in the metazoan nervous system and identify a poly(A) RNA binding protein associated with a human brain disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

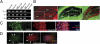

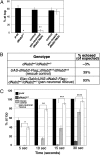

References
-
- Ropers HH. Genetics of intellectual disability. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18:241–250. - PubMed
-
- Najmabadi H, et al. Homozygosity mapping in consanguineous families reveals extreme heterogeneity of non-syndromic autosomal recessive mental retardation and identifies 8 novel gene loci. Hum Genet. 2007;121:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Kuss AW, et al. Autosomal recessive mental retardation: Homozygosity mapping identifies 27 single linkage intervals, at least 14 novel loci and several mutation hotspots. Hum Genet. 2011;129:141–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

