Optimization of dosing for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with evolutionary cancer modeling
- PMID: 21734175
- PMCID: PMC3500629
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002356
Optimization of dosing for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with evolutionary cancer modeling
Abstract
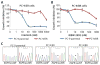
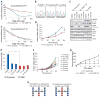
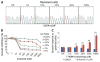
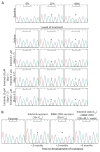
Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) that harbor mutations within the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene are sensitive to the tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) gefitinib and erlotinib. Unfortunately, all patients treated with these drugs will acquire resistance, most commonly as a result of a secondary mutation within EGFR (T790M). Because both drugs were developed to target wild-type EGFR, we hypothesized that current dosing schedules were not optimized for mutant EGFR or to prevent resistance. To investigate this further, we developed isogenic TKI-sensitive and TKI-resistant pairs of cell lines that mimic the behavior of human tumors. We determined that the drug-sensitive and drug-resistant EGFR-mutant cells exhibited differential growth kinetics, with the drug-resistant cells showing slower growth. We incorporated these data into evolutionary mathematical cancer models with constraints derived from clinical data sets. This modeling predicted alternative therapeutic strategies that could prolong the clinical benefit of TKIs against EGFR-mutant NSCLCs by delaying the development of resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non–small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, Mardis E, Kupfer D, Wilson R, Kris M, Varmus H. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:13306–13311. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mulloy R, Ferrand A, Kim Y, Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Anderson KS, Settleman J. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutants from human lung cancers exhibit enhanced catalytic activity and increased sensitivity to gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2325–2330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

