Deep sequencing of the human TCRγ and TCRβ repertoires suggests that TCRβ rearranges after αβ and γδ T cell commitment
- PMID: 21734177
- PMCID: PMC4179204
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002536
Deep sequencing of the human TCRγ and TCRβ repertoires suggests that TCRβ rearranges after αβ and γδ T cell commitment
Abstract
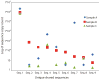
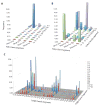
T lymphocytes respond to a broad array of pathogens with the combinatorial diversity of the T cell receptor (TCR). This adaptive response is possible because of the unique structure of the TCR, which is composed of two chains, either αβ or γδ, that undergo genetic rearrangement in the thymus. αβ and γδ T cells are functionally distinct within the host but are derived from a common multipotent precursor. The canonical model for T cell lineage commitment assumes that the γ, δ, and β chains rearrange before αβ or γδ T cell commitment. To test the standard model in humans, we used high-throughput sequencing to catalog millions of TCRγ and TCRβ chains from peripheral blood αβ and γδ T cells from three unrelated individuals. Almost all sampled αβ and γδ T cells had rearranged TCRγ sequences. Although sampled αβ T cells had a diverse repertoire of rearranged TCRβ chains, less than 4% of γδ T cells in peripheral blood had a rearranged TCRβ chain. Our data suggest that TCRγ rearranges in all T lymphocytes, consistent with TCRγ rearranging before T cell lineage commitment. However, rearrangement of the TCRβ locus appears to be restricted after T cell precursors commit to the αβ T cell lineage. Indeed, in T cell leukemias and lymphomas, TCRγ is almost always rearranged and TCRβ is only rearranged in a subset of cancers. Because high-throughput sequencing of TCRs is translated into the clinic for monitoring minimal residual for leukemia/lymphoma, our data suggest the sequencing target should be TCRγ.
Figures


References
-
- Brenner MB, McLean J, Dialynas DP, Strominger JL, Smith JA, Owen FL, Seidman JG, Ip S, Rosen F, Krangel MS. Identification of a putative second T-cell receptor. Nature. 1986;322:145. - PubMed
-
- Allison J, McIntyre B, Bloch D. Tumor-specific antigen of murine T-lymphoma defined with monoclonal antibody. The Journal of Immunology. 1982;129:2293. published online Epub November 1, 1982 ( - PubMed
-
- Hayday AC. gamma delta cells: A right time and a right place for a conserved third way of protection. Annual Review of Immunology. 2000;18:975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

