Residues 248-252 and 300-304 of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger are involved in its regulation by phospholemman
- PMID: 21734189
- PMCID: PMC3191572
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00069.2011
Residues 248-252 and 300-304 of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger are involved in its regulation by phospholemman
Abstract
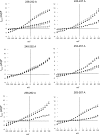
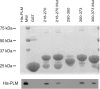
Using split cardiac Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchangers (NCX1), we previously demonstrated that phospholemman (PLM) regulates NCX1 by interacting with the proximal linker domain (residues 218-358) of the intracellular loop of NCX1. With the use of overlapping loop deletion mutants, interaction sites are localized to two regions spanning residues 238-270 and residues 300-328 of NCX1. In this study, we used alanine (Ala) linker scanning to pinpoint the residues in the proximal linker domain involved in regulation of NCX1 by PLM. Transfection of human embryonic kidney (HEK)293 cells with wild-type (WT) NCX1 or its Ala mutants but not empty vector resulted in NCX1 current (I(NaCa)). Coexpression of PLM with WT NCX1 inhibited I(NaCa). Mutating residues 248-252 (PASKT) or 300-304 (QKHPD) in WT NCX1 to Ala resulted in loss of inhibition of I(NaCa) by PLM. By contrast, inhibition of I(NaCa) by PLM was preserved when residues 238-242, 243-247, 253-257, 258-262, 263-267, 305-309, 310-314, 315-319, 320-324, or 325-329 were mutated to Ala. While mutating residue 301 to alanine completely abolished PLM inhibition, mutation of any single residue 250-252, 300, or 302-304 resulted in partial reduction in inhibition. Mutating residues 248-252 to Ala resulted in significantly weaker association with PLM. The NCX1-G503P mutant that lacks Ca(2+)-dependent activation retained its sensitivity to PLM. We conclude that residues 248-252 and 300-304 in the proximal linker domain of NCX1 were involved in its inhibition by PLM.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phospholemman regulates cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger by interacting with the exchanger's proximal linker domain.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Apr;296(4):C911-21. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00196.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19158404 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholemman inhibition of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Role of phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 24;281(12):7784-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512092200. Epub 2006 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16434394 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic tail of phospholemman interacts with the intracellular loop of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 20;281(42):32004-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606876200. Epub 2006 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16921169 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated regulation of cardiac Na(+)/Ca (2+) exchanger and Na (+)-K (+)-ATPase by phospholemman (FXYD1).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:175-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224879 Review.
-
Regulation of cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger by phospholemman.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Mar;1099:119-34. doi: 10.1196/annals.1387.004. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17446450 Review.
Cited by
-
"Oxygen Sensing" by Na,K-ATPase: These Miraculous Thiols.Front Physiol. 2016 Aug 2;7:314. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00314. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27531981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of a Proteolytically Stable Sodium-Calcium Exchanger 1 Activator Peptide for In Vivo Studies.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 7;12:638646. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.638646. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34163352 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a high-affinity peptide that prevents phospholemman (PLM) inhibition of the sodium/calcium exchanger 1 (NCX1).Biochem J. 2016 Aug 1;473(15):2413-23. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160465. Epub 2016 May 31. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27247424 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Phosphatase 1c Associated with the Cardiac Sodium Calcium Exchanger 1 Regulates Its Activity by Dephosphorylating Serine 68-phosphorylated Phospholemman.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 26;291(9):4561-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.677898. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26668322 Free PMC article.
-
The Na+/K+ pump dominates control of glycolysis in hippocampal dentate granule cells.Elife. 2022 Oct 12;11:e81645. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81645. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36222651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlers BA, Zhang XQ, Moorman JR, Rothblum LI, Carl LL, Song J, Wang J, Geddis LM, Tucker AL, Mounsey JP, Cheung JY. Identification of an endogenous inhibitor of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, phospholemman. J Biol Chem 280: 19875–19882, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Beevers AJ, Kukol A. Phospholemman transmembrane structure reveals potential interactions with Na+/K+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 282: 32742–32748, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bers DM. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature 415: 198–205, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Bossuyt J, Ai X, Moorman JR, Pogwizd SM, Bers DM. Expression and phosphorylation of the Na-pump regulatory subunit phospholemman in heart failure. Circ Res 97: 558–565, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Cheung JY, Rothblum LI, Moorman JR, Tucker AL, Song J, Ahlers BA, Carl LL, Wang J, Zhang XQ. Regulation of cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger by phospholemman. Ann NY Acad Sci 1099: 119–134, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

