Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor reverses alcohol-induced allostasis of the mesolimbic dopaminergic system: implications for alcohol reward and seeking
- PMID: 21734280
- PMCID: PMC3144766
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1750-11.2011
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor reverses alcohol-induced allostasis of the mesolimbic dopaminergic system: implications for alcohol reward and seeking
Abstract
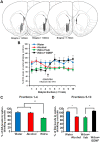
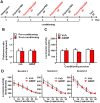
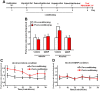
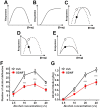
We previously showed that infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) into the ventral tegmental area (VTA) rapidly reduces alcohol intake and relapse (Carnicella et al., 2008, 2009a), and increases dopamine (DA) levels in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of alcohol-naive rats (Wang et al., 2010). Withdrawal from excessive alcohol intake is associated with a reduction in NAc DA levels, whereas drug-induced increases in NAc DA levels are associated with reward. We therefore tested whether GDNF in the VTA reverses alcohol withdrawal-associated DA deficiency and/or possesses rewarding properties. Rats were trained for 7 weeks to consume high levels of alcohol (5.47 ± 0.37 g/kg/24 h) in intermittent access to 20% alcohol in a two-bottle choice procedure. Using in vivo microdialysis, we show that 24 h withdrawal from alcohol causes a substantial reduction in NAc DA overflow, which was reversed by intra-VTA GDNF infusion. Using conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm, we observed that GDNF on its own does not induce CPP, suggesting that the growth factor is not rewarding. However, GDNF blocked acquisition and expression of alcohol-CPP. In addition, GDNF induced a downward shift in the dose-response curve for operant self-administration of alcohol, further suggesting that GDNF suppresses, rather than substitutes for, the reinforcing effects of alcohol. Our findings suggest that GDNF reduces alcohol-drinking behaviors by reversing an alcohol-induced allostatic DA deficiency in the mesolimbic system. In addition, as it lacks abuse liability, the study further highlights GDNF as a promising target for treatment of alcohol use/abuse disorders.
Figures

Comment in
-
Alcohol reward, dopamine depletion, and GDNF.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 19;31(42):14833-4. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4222-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22016515 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. Transition from moderate to excessive drug intake: change in hedonic set point. Science. 1998;282:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. Transition to drug addiction: a negative reinforcement model based on an allostatic decrease in reward function. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;180:473–490. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:383–394. - PubMed
-
- Bailey CP, O'Callaghan MJ, Croft AP, Manley SJ, Little HJ. Alterations in mesolimbic dopamine function during the abstinence period following chronic ethanol consumption. Neuropharmacology. 2001;41:989–999. - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
