Clinical trial of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children and young adults
- PMID: 21734640
- PMCID: PMC3306824
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.195
Clinical trial of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children and young adults
Abstract
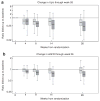
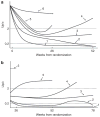
This NIH-funded multicenter randomized study of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) treatment compared the efficacy of a 12-month course of cyclosporine to a combination of oral pulse dexamethasone and mycophenolate mofetil in children and adults with steroid-resistant primary FSGS. Of the 192 patients enrolled, 138 were randomized to cyclosporine (72) or to mycophenolate/dexamethasone (66). The primary analysis compared the levels of an ordinal variable measuring remission during the first year. The odds ratio (0.59) for achieving at least a partial remission with mycophenolate/dexamethasone compared to cyclosporine was not significant. Partial or complete remission was achieved in 22 mycophenolate/dexamethasone- and 33 cyclosporine-treated patients at 12 months. The main secondary outcome, preservation of remission for 26 weeks following cessation of treatment, was not significantly different between these two therapies. During the entire 78 weeks of study, 8 patients treated with cyclosporine and 7 with mycophenolate/dexamethasone died or developed kidney failure. Thus, our study did not find a difference in rates of proteinuria remission following 12 months of cyclosporine compared to mycophenolate/dexamethasone in patients with steroid-resistant FSGS. However, the small sample size might have prevented detection of a moderate treatment effect.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00135811.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immunosuppressive treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: lessons from a randomized controlled trial.Kidney Int. 2011 Oct;80(8):798-801. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.191. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 21960168
References
-
- Troyanov S, Wall CA, Miller JA, et al. Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis: definition and relevance of a partial remission. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1061–1068. - PubMed
-
- Gipson DS, Chin H, Presler TP, et al. Differential risk of remission and ESRD in childhood FSGS. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:344–349. - PubMed
-
- Rydel JJ, Korbet SM, Borok RZ, et al. Focal segmental glomerular sclerosis in adults: presentation, course, and response to treatment. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;25:534–542. - PubMed
-
- Abrantes MM, Cardoso LSB, Lima EM, et al. Predictive factors of chronic kidney disease in primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:1003–1012. - PubMed
-
- Bakir AA, Share DS, Levy PS, et al. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adult African Americans. Clin Nephrol. 1996;46:306–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

