Sonographic features of duodenal lipomas in eight clinicopathologically diagnosed patients
- PMID: 21734794
- PMCID: PMC3120946
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2855
Sonographic features of duodenal lipomas in eight clinicopathologically diagnosed patients
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the sonographic features and diagnostic value of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) for duodenal lipomas (DLs).
Methods: A total of eight consecutive patients with DL diagnosed pathologically were included in the study. One EUS expert reviewed the ultrasonic images for all lesions, including the original layer of the duodenal wall, the echo intensity and the echo homogeneity. The size of the lesions and the perifocal structures were also investigated. The diagnosis by EUS was compared with the histological results.
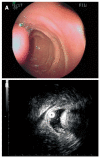
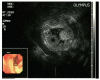
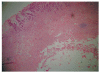
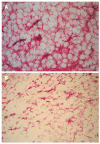
Results: Using routine endoscopy, only one case was correctly diagnosed as DL. Four cases were classified as submucosal tumors, and three cases were mistaken for stromal tumors. All tumors appeared as round or oval intensive hyperechoic lesions with distinct anterior borders that originated from the submucosal layer on EUS. Tumors ranged from 8 to 36 mm in size, with an average size of 16 mm. Homogeneous echogenicity was seen in all cases except one that had a tubular structure inside the tumor. Echo attenuation was observed only in the area behind the tumors in five cases, and it was observed both inside and behind the tumors in three cases in which the posterior border was obscure or invisible. Seven (87.5%) cases were correctly diagnosed as DL, and one (12.5%) was mistaken as Brunner's gland adenoma by EUS. Pathologically, all tumors originated from the submucosal layer and consisted of mature fat cells without heteromorphism. Among the fat cells, there was a small amount of thick-wall vessels infiltrating the lymphocytes, and abundant fibrous connective tissues.
Conclusion: On EUS, DL is featured as an intensive homogeneous hyperechoic submucosal lesion with marked echo attenuation and without involvement of the mucosa.
Keywords: Duodenum; Echo attenuation; Endoscopic ultrasonography; Hyperecho; Lipoma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors treatment and value of endoscopic ultrasonography in pre-operation assess and post-operation follow-up: a prospective study of 224 cases in a single medical center.Surg Endosc. 2016 Oct;30(10):4206-13. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4729-1. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26823060
-
Endoscopic ultrasound for differential diagnosis of duodenal lesions.Ultraschall Med. 2012 Dec;33(7):E210-E217. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1313135. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Ultraschall Med. 2012. PMID: 23129520
-
Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography for rectal neuroendocrine neoplasms.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10470-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10470. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132764 Free PMC article.
-
Brunner's gland adenoma of duodenum: report of two cases.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):7565-9. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[X-ray computed tomography of duodenal lipoma].J Radiol. 1992 Jun-Jul;73(6-7):395-8. J Radiol. 1992. PMID: 1474513 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Laparoscopic management of a large duodenal lipoma presented as gastric outlet obstruction.JSLS. 2013 Jul-Sep;17(3):459-62. doi: 10.4293/108680813X13654754535395. JSLS. 2013. PMID: 24018087 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Duodenal Lipoma: A Systematic Review and a Case Report.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Jul;11(7):PE01-PE05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/27748.10322. Epub 2017 Jul 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28892976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spontaneous expulsion of a duodenal lipoma after endoscopic biopsy: A case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 14;28(34):5086-5092. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.5086. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36160650 Free PMC article.
-
Duodenal subepithelial hyperechoic lesions of the third layer: Not always a lipoma.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2013 Oct 16;5(10):514-8. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.514. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2013. PMID: 24147196 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging features of multiple duodenal lipomas: a rare cause of intestinal obstruction.Jpn J Radiol. 2012 Oct;30(8):676-9. doi: 10.1007/s11604-012-0098-z. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Jpn J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22752443
References
-
- Taylor AJ, Stewart ET, Dodds WJ. Gastrointestinal lipomas: a radiologic and pathologic review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;155:1205–1210. - PubMed
-
- Sou S, Nomura H, Takaki Y, Nagahama T, Matsubara F, Matsui T, Yao T. Hemorrhagic duodenal lipoma managed by endoscopic resection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:479–481. - PubMed
-
- Blanchet MC, Arnal E, Paparel P, Grima F, Voiglio EJ, Caillot JL. Obstructive duodenal lipoma successfully treated by endoscopic polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:938–939. - PubMed
-
- Tung CF, Chow WK, Peng YC, Chen GH, Yang DY, Kwan PC. Bleeding duodenal lipoma successfully treated with endoscopic polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:116–117. - PubMed
-
- Hizawa K, Kawasaki M, Kouzuki T, Aoyagi K, Fujishima M. Unroofing technique for the endoscopic resection of a large duodenal lipoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:391–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

