Pseudopneumoperitoneum in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: a case report
- PMID: 21734810
- PMCID: PMC3129513
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i24.2972
Pseudopneumoperitoneum in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: a case report
Abstract
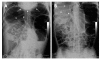
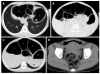
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) is a rare disease due to a severe gastrointestinal motility disorder which may mimic, on both clinical and radiological grounds, mechanical obstruction. We report a case of a 26-year-old woman who presented to our institution for plain abdominal radiography for referred long-lasting constipation with recurrent episodes of abdominal pain and distension. At X-ray, performed both in the upright and supine position, an isolated air-fluid level was depicted in the left flank, together with a number of radiological signs suggestive of pneumoperitoneum. First, subphrenic radiolucency could be observed in the upright film. Second, the intestinal wall of some jejunal loops appeared to be outlined in the right flank. Third, the inferior cardiac border was clearly depicted in the upright film. The patient however had no evidence of peritoneal signs but only hypoactive bowel movements. Unenhanced multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) of the abdomen and pelvis was therefore performed. MDCT revealed abnormal air-driven distension of the small and large bowel, without evidence of extra-luminal air. All radiological signs of pneumoperitoneum turned out to be false-positive results. The patient was submitted to pan-colonoscopy and to anorectal manometry to rule out Hirshprung's disease, and was finally discharged with a diagnosis of CIPO.
Keywords: Abdominal radiography; Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction; Motility disorders; Multi-detector computed tomography; Pseudopneumoperitoneum.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A case of spontaneous pneumoperitoneum associated with idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009 Dec;54(6):395-8. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2009.54.6.395. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 20026895 Korean.
-
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adult patients: multidetector row helical CT features.Eur Radiol. 2008 Aug;18(8):1587-95. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-0913-1. Epub 2008 Mar 21. Eur Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18357454 Review.
-
Pneumatosis and pneumoperitoneum in chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction.J Pediatr Surg. 1991 Dec;26(12):1384-6. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(91)91039-2. J Pediatr Surg. 1991. PMID: 1765913
-
CHRONIC PSEUDO-OBSTRUCTION OF THE SIGMOID COLON: A CASE REPORT.Acta Clin Croat. 2022 Dec;61(4):735-740. doi: 10.20471/acc.2022.61.04.23. Acta Clin Croat. 2022. PMID: 37868188 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction.Dig Dis. 1995 May-Jun;13(3):163-81. doi: 10.1159/000171499. Dig Dis. 1995. PMID: 8548980 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of enhanced recovery program for patients undergoing partial laparoscopic hepatectomy of liver cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Sep;17(9):694-701. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1296-9. Epub 2015 May 22. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25997686 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Stanghellini V, Cogliandro RF, De Giorgio R, Barbara G, Morselli-Labate AM, Cogliandro L, Corinaldesi R. Natural history of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adults: a single center study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:449–458. - PubMed
-
- Merlin A, Soyer P, Boudiaf M, Hamzi L, Rymer R. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adult patients: multidetector row helical CT features. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:1587–1595. - PubMed
-
- Miller RE. The radiological evaluation of intraperitoneal gas (pneumoperitoneum) CRC Crit Rev Clin Radiol Nucl Med. 1973;4:61–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

