Dopamine and paraquat enhance α-synuclein-induced alterations in membrane conductance
- PMID: 21735318
- PMCID: PMC3175296
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-011-9255-x
Dopamine and paraquat enhance α-synuclein-induced alterations in membrane conductance
Abstract
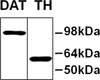
We have previously demonstrated that α-synuclein overexpression increases the membrane conductance of dopaminergic-like cells. Although α-synuclein is thought to play a central role in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, and diffuse Lewy body disease, the mechanism of action is not completely understood. In this study, we sought to determine whether multiple factors act together with α-synuclein to engender cell vulnerability through an augmentation of membrane conductance. In this article, we employed a cell model that mimics dopaminergic neurons coupled with α-synuclein overexpression and oxidative stressors. We demonstrate an enhancement of α-synuclein-induced toxicity in the presence of combined treatment with dopamine and paraquat, two molecules known to incite oxidative stress. In addition, we show that combined dopamine and paraquat treatment increases the expression of heme oxygenase-1, an antioxidant response protein. Finally, we demonstrate for the first time that combined treatment of dopaminergic cells with paraquat and dopamine enhances α-synuclein-induced leak channel properties resulting in increased membrane conductance. Importantly, these increases are most robust when both paraquat and dopamine are present suggesting the need for multiple oxidative insults to augment α-synuclein-induced disruption of membrane integrity.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Progressive neurodegenerative and behavioural changes induced by AAV-mediated overexpression of α-synuclein in midbrain dopamine neurons.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Mar;45(3):939-53. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.013. Epub 2011 Dec 11. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22182688
-
Dysregulated dopamine storage increases the vulnerability to α-synuclein in nigral neurons.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Sep;47(3):367-77. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.05.012. Epub 2012 May 31. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22659302
-
Interplay between cytosolic dopamine, calcium, and alpha-synuclein causes selective death of substantia nigra neurons.Neuron. 2009 Apr 30;62(2):218-29. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.01.033. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19409267 Free PMC article.
-
Does alpha-synuclein modulate dopaminergic synaptic content and tone at the synapse?FASEB J. 2004 Apr;18(6):637-47. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-1112rev. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15054086 Review.
-
Could a loss of alpha-synuclein function put dopaminergic neurons at risk?J Neurochem. 2004 Jun;89(6):1318-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02423.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15189334 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of neurotoxicants and traumatic brain injury in α-synuclein protein misfolding and aggregation.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Jul;133:60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.12.003. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 27993598 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Events Leading to Paraquat-Induced Apoptosis: Mechanistic Insights into Parkinson's Disease Pathophysiology.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jun;59(6):3353-3369. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02799-2. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35306641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental neurotoxic challenge of conditional alpha-synuclein transgenic mice predicts a dopaminergic olfactory-striatal interplay in early PD.Acta Neuropathol. 2014 Apr;127(4):477-94. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1255-5. Epub 2014 Feb 8. Acta Neuropathol. 2014. PMID: 24509835 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent models and contemporary molecular techniques: notable feats yet incomplete explanations of Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Oct;46(2):495-512. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8291-8. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22736079 Review.
-
Parkinson's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:389-455. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_16. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Fariñas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho W-H, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JMG, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Phillips H, Sulzer D, Rosenthal A. Mice Lacking [alpha]-Synuclein Display Functional Deficits in the Nigrostriatal Dopamine System. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Alam ZI, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Marsden DC, Jenner P, Halliwell B. A Generalised Increase in Protein Carbonyls in the Brain in Parkinson's but Not Incidental Lewy Body Disease. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1997a;69:1326–1329. - PubMed
-
- Alam ZI, Jenner A, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Cairns N, Marsden CD, Jenner P, Halliwell B. Oxidative DNA Damage in the Parkinsonian Brain: An Apparent Selective Increase in 8-Hydroxyguanine Levels in Substantia Nigra. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1997b;69:1196–1203. - PubMed
-
- Auluck PK, Caraveo G, Lindquist S. α-Synuclein: Membrane Interactions and Toxicity in Parkinson's Disease. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 2010;26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

