ClpXP, an ATP-powered unfolding and protein-degradation machine
- PMID: 21736903
- PMCID: PMC3209554
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.06.007
ClpXP, an ATP-powered unfolding and protein-degradation machine
Abstract
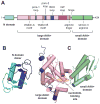
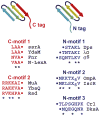
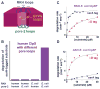
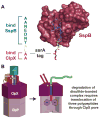
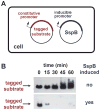
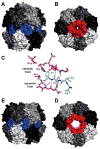
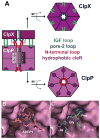
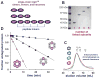
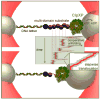
ClpXP is a AAA+ protease that uses the energy of ATP binding and hydrolysis to perform mechanical work during targeted protein degradation within cells. ClpXP consists of hexamers of a AAA+ ATPase (ClpX) and a tetradecameric peptidase (ClpP). Asymmetric ClpX hexamers bind unstructured peptide tags in protein substrates, unfold stable tertiary structure in the substrate, and then translocate the unfolded polypeptide chain into an internal proteolytic compartment in ClpP. Here, we review our present understanding of ClpXP structure and function, as revealed by two decades of biochemical and biophysical studies.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


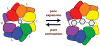
References
-
- Hanson PI, Whiteheart SW. AAA+ proteins: have engine, will work. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:519–529. - PubMed
-
- Sauer RT, Baker TA. AAA+ proteases: ATP-fueled machines of protein destruction. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011 Jun 23; [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Katayama-Fujimura Y, Gottesman S, Maurizi MR. A multiple-component, ATP-dependent protease from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:4477–4485. - PubMed
-
- Katayama Y, Gottesman S, Pumphrey J, Rudikoff S, Clark WP, Maurizi MR. The two-component, ATP-dependent Clp protease of Escherichia coli. Purification, cloning, and mutational analysis of the ATP-binding component. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:15226–15236. - PubMed
-
- Hwang BJ, Woo KM, Goldberg AL, Chung CH. Protease Ti, a new ATP-dependent protease in Escherichia coli,contains protein-activated ATPase and proteolytic functions in distinct subunits. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:8727–8734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

