DLK1-DIO3 genomic imprinted microRNA cluster at 14q32.2 defines a stemlike subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with poor survival
- PMID: 21737452
- PMCID: PMC3162431
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.229831
DLK1-DIO3 genomic imprinted microRNA cluster at 14q32.2 defines a stemlike subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with poor survival
Abstract
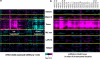
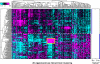
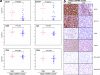
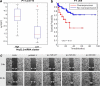
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a heterogeneous and highly aggressive malignancy, for which there are no effective cures. Identification of a malignant stemlike subtype of HCC may offer patients with a dismal prognosis a potential targeted therapy using c-MET and Wnt pathway inhibitors. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) show promise as diagnostic and prognostic tools for cancer detection and stratification. Using a TRE-c-Met-driven transgenic HCC mouse model, we identified a cluster of 23 miRNAs that is encoded within the Dlk1-Gtl2 imprinted region on chromosome 12qF1 overexpressed in all of the isolated liver tumors. Interestingly, this region is conserved among mammalian species and maps to the human DLK1-DIO3 region on chromosome 14q32.2. We thus examined the expression of the DLK1-DIO3 miRNA cluster in a cohort of 97 hepatitis B virus-associated HCC patients and identified a subgroup (n = 18) of patients showing strong coordinate overexpression of miRNAs in this cluster but not in other cancer types (breast, lung, kidney, stomach, and colon) that were tested. Expression levels of imprinted gene transcripts from neighboring loci in this 14q32.2 region and from a subset of other imprinted sites were concomitantly elevated in human HCC. Interestingly, overexpression of the DLK1-DIO3 miRNA cluster was positively correlated with HCC stem cell markers (CD133, CD90, EpCAM, Nestin) and associated with a high level of serum α-fetoprotein, a conventional biomarker for liver cancer, and poor survival rate in HCC patients. In conclusion, our findings suggest that coordinate up-regulation of the DLK1-DIO3 miRNA cluster at 14q32.2 may define a novel molecular (stem cell-like) subtype of HCC associated with poor prognosis.
Figures

References
-
- Parkin D. M., Bray F., Ferlay J., Pisani P. (2005) CA Cancer J. Clin. 55, 74–108 - PubMed
-
- Lee T. K., Castilho A., Ma S., Ng I. O. (2009) Liver Int. 29, 955–965 - PubMed
-
- Yang Z. F., Ho D. W., Ng M. N., Lau C. K., Yu W. C., Ngai P., Chu P. W., Lam C. T., Poon R. T., Fan S. T. (2008) Cancer Cell 13, 153–166 - PubMed
-
- Ma S., Lee T. K., Zheng B. J., Chan K. W., Guan X. Y. (2008) Oncogene 27, 1749–1758 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

