Is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus replacing methicillin-susceptible S. aureus?
- PMID: 21737459
- PMCID: PMC3172038
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkr278
Is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus replacing methicillin-susceptible S. aureus?
Abstract
Despite extensive research on the emergence of and treatments for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), prior studies have not rigorously evaluated the impact of methicillin resistance on the overall incidence of S. aureus infections. Yet, there are direct clinical and research implications of determining whether methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) infection rates remain stable in the face of increasing MRSA prevalence or whether MSSA will be replaced over time. A synthesis of prior studies indicates that the emergence of healthcare-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA) and community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) has led to an increase in the overall incidence of S. aureus infections, with MRSA principally adding to, rather than replacing, MSSA. However, colonization with CA-MRSA may at least partially replace colonization with MSSA. So far, evidence indicates that MSSA still accounts for many infections. Therefore, eradication of MRSA alone is not sufficient to address the public health burden of S. aureus.
Figures
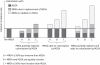

References
-
- Wertheim HF, Melles DC, Vos MC, et al. The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:751–62. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70295-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:520–32. doi:10.1056/NEJM199808203390806. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deurenberg RH, Stobberingh EE. The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Genet Evol. 2008;8:747–63. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Strommenger B, Braulke C, Heuck D, et al. spa typing of Staphylococcus aureus as a frontline tool in epidemiological typing. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:574–81. doi:10.1128/JCM.01599-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

