Podocyte COX-2 exacerbates diabetic nephropathy by increasing podocyte (pro)renin receptor expression
- PMID: 21737546
- PMCID: PMC3137572
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010111149
Podocyte COX-2 exacerbates diabetic nephropathy by increasing podocyte (pro)renin receptor expression
Abstract
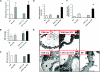
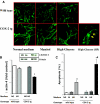
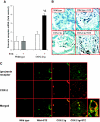
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) increases podocyte cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, and COX-2 inhibition reduces proteinuria and glomerular injury in animal models of diabetes. To investigate the role of podocyte COX-2 in development of diabetic nephropathy, we employed a streptozotocin model of diabetic mellitus in wild-type and transgenic mice expressing COX-2 selectively in podocytes. Progressive albuminuria developed only in diabetic COX-2 transgenic mice despite hyperglycemia, BP, and GFR being similar to those in wild-type mice. Transgenic mice also manifested significant foot-process effacement, moderate mesangial expansion, and segmental thickening of the glomerular basement membrane. In cultured podocytes overexpressing COX-2, high glucose induced cell injury and increased both expression of the pro(renin) receptor and activation of the renin-angiotensin system. Downregulation of the (pro)renin receptor attenuated the injury induced by high glucose. In vivo, podocyte pro(renin) receptor expression increased in diabetic COX-2-transgenic mice, and treatment with a COX-2 inhibitor abrogated the upregulation of (pro)renin receptor and reduced albuminuria, foot-process effacement, and mesangial matrix expansion. In summary, these results demonstrate that increased expression of podocyte COX-2 predisposes to diabetic glomerular injury and that the (pro)renin receptor may be one mediator for this increased susceptibility to injury.
Copyright © 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology
Figures





References
-
- Tan AL, Forbes JM, Cooper ME: AGE, RAGE, and ROS in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27: 130–143, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Kanwar YS, Wada J, Sun L, Xie P, Wallner EI, Chen S, Chugh S, Danesh FR: Diabetic nephropathy: Mechanisms of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233: 4–11, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Marshall SM: The podocyte: A major player in the development of diabetic nephropathy? Horm Metab Res 37 [Suppl 1]: 9–16, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Marshall SM: The podocyte: A potential therapeutic target in diabetic nephropathy? Curr Pharm Des 13: 2713–2720, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Reddy GR, Kotlyarevska K, Ransom RF, Menon RK: The podocyte and diabetes mellitus: Is the podocyte the key to the origins of diabetic nephropathy? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17: 32–36, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

