Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis caused by diltiazem
- PMID: 21738378
- PMCID: PMC3119988
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2011.23.1.108
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis caused by diltiazem
Abstract
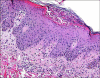
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is clinically characterized by fever, pruritus and an acute pustular eruption. It can be described as having an abrupt onset and then spontaneous resolution occurs shortly after the start of symptoms, and there is usually only a single episode. Most cases have been triggered by the ingestion of drugs. Diltiazem hydrochloride is a calcium channel blocker that is commonly used for treating hypertension and angina. This drug was found to be the responsible agent in our current patient. There have been 9 such case reports in the English medical literature, yet this is the first such report in the Korean medical literature. We present the case of a 51-year-old male who experienced an acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to diltiazem hydrochloride and we review the relevant literature.
Keywords: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; Diltiazem; Drug reaction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Drugs associated with acute generalized exanthematic pustulosis].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2003 Jun-Jul;130(6-7):612-8. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2003. PMID: 13679697 Review. French.
-
Diltiazem-induced acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis.Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995 Jul;20(4):341-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1995.tb01339.x. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995. PMID: 8548996
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by icotinib: a case report and literature review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1462430. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1462430. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39281279 Free PMC article.
-
A Pediatric Case of Acute Generalized Pustular Eruption without Streptococcal Infection.Case Rep Dermatol. 2016 Jun 13;8(2):173-8. doi: 10.1159/000446691. eCollection 2016 May-Aug. Case Rep Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27462226 Free PMC article.
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: report of 12 cases and literature review.Int J Dermatol. 2009 Mar;48(3):253-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.03908.x. Int J Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19261012 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug Triggers and Clinic of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP): A Literature Case Series of 297 Patients.J Clin Med. 2022 Jan 13;11(2):397. doi: 10.3390/jcm11020397. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35054090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrochlorothizide-induced acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis presenting with bilateral periorbital impetigo.BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Feb 11;12(2):e223528. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223528. BMJ Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30755424 Free PMC article.
-
Multisystem organ failure secondary to acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) with atypical presentation resembling septic shock.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 Mar 1;15(3):e247040. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-247040. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35232738 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiodermatology: the heart of the connection between the skin and cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025 May;22(5):354-371. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01097-9. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39537837 Review.
References
-
- Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1333–1338. - PubMed
-
- Beylot C, Doutre MS, Beylot-Barry M. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15:244–249. - PubMed
-
- Breathnach SM. Drug reaction. In: Champion RH, Burton JL, Burns DA, Breathnach SM, editors. Rook/Wilkinson/Ebling textbook of dermatology. 6th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1998. pp. 3349–3517.
-
- Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR) Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:989–996. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

