Complement gene expression and regulation in mouse retina and retinal pigment epithelium/choroid
- PMID: 21738388
- PMCID: PMC3123163
Complement gene expression and regulation in mouse retina and retinal pigment epithelium/choroid
Abstract
Purpose: To understand the expression of genes involved in different complement pathways in the retina and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)/choroid under physiologic conditions and how their expression is regulated by inflammatory cytokines.
Methods: The expression of complement components of the classical pathway (CP), mannose-binding lectin (MBL) pathway, alternative pathway (AP), and terminal pathway in the retina and RPE/choroid was determined by conventional reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The effect of inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α, 20 ng/ml), interleukin (IL)-6 (10 ng/ml), interferon-gamma (IFN-γ, 100 ng/ml) or lipopolysaccharides (LPS, 1 μg/ml) on the expression of these complement component genes was tested in vitro in primary cultured RPE cells and a microglial cell line (BV2 cells) and quantified by real-time RT-PCR.
Results: In the CP, complements C1qb, C1r, C1s, C2, and C4 were constitutively expressed by retina and RPE/choroid. Complement factor H and factor B of the AP as well as C3 were also detected in the retinal and RPE/choroidal tissues. In the MBL pathway, low levels of mannose-binding lectin (MBL)-associated serine protease (MASP)-1 in the retina and RPE/choroid and MASP2L in the retina were detected. Other components, including mannose-binding lectin 1 (MBL1), mannose-binding lectin 2 (MBL2), complement factor I (CFI), complement component 5 (C5) and complement factor H-related protein 1 (CFHR1), were not detected in either the retina or the RPE/choroid. The expression of CP- and AP-complement component genes in RPE and microglial cells was upregulated by interferon (IFN)-γ treatment. Treatment with TNF-α selectively upregulated the expression of C1s and C3 genes but downregulated complement factor H gene expression in RPE and microglial cells. The expression of genes involved in the MBL pathway was not affected by the inflammatory cytokines tested in this study.
Conclusions: Retina and RPE/choroid express a variety of complement components that are involved mainly in the CP and AP. RPE and microglial cells are the main sources of retinal complement gene expression. Retinal complement gene expression is regulated by inflammatory cytokines, such as IFN-γ and TNF-α.
Figures
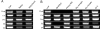
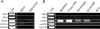
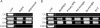
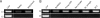
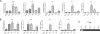
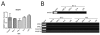


References
-
- Zhang C, Lam T, Tso M. Heterogeneous populations of microglia/macrophages in the retina and their activation after retinal ischemia and reperfusion injury. Exp Eye Res. 2005;81:700–9. - PubMed
-
- Dick AD, Carter D, Robertson M, Broderick C, Hughes E, Forrester JV, Liversidge J. Control of myeloid activity during retinal inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;74:161–6. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Chen M, Forrester JV. Para-inflammation in the aging retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2009;28:348–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
