Acute demyelinating disease after oral therapy with herbal extracts
- PMID: 21738505
- PMCID: PMC3130893
- DOI: 10.1159/000329734
Acute demyelinating disease after oral therapy with herbal extracts
Abstract
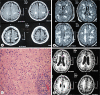
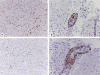
Central nervous system demyelinating processes such as multiple sclerosis and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis constitute a group of diseases not completely understood in their physiopathology. Environmental and toxic insults are thought to play a role in priming autoimmunity. The aim of the present report is to describe a case of acute demyelinating disease with fatal outcome occurring 15 days after oral exposure to herbal extracts.
Keywords: Demyelinating disease; Immunostimulant; Phytomedicine.
Figures
References
-
- Filley CM, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK. Toxic leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Tenembaum S, Chamoles N, Fejerman N. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: a long-term follow-up study of 84 pediatric patients. Neurology. 2002;59:1224–1231. - PubMed
-
- de Seze J, Debouverie M, Zephir H, et al. Acute fulminant demyelinating disease: a descriptive study of 60 patients. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:1426–1432. - PubMed
-
- Tenembaum S, Chitnis T, Ness J, Hahn JS. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neurology. 2007;68:S23–S36. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

