Selective BRAFV600E inhibitor PLX4720, requires TRAIL assistance to overcome oncogenic PIK3CA resistance
- PMID: 21738740
- PMCID: PMC3124547
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021632
Selective BRAFV600E inhibitor PLX4720, requires TRAIL assistance to overcome oncogenic PIK3CA resistance
Abstract
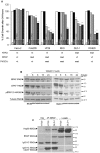
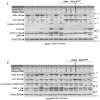
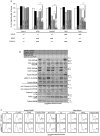
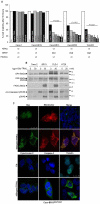
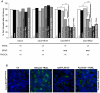
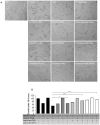
Documented sensitivity of melanoma cells to PLX4720, a selective BRAFV600E inhibitor, is based on the presence of mutant BRAF(V600E) alone, while wt-BRAF or mutated KRAS result in cell proliferation. In colon cancer appearance of oncogenic alterations is complex , since BRAF, like KRAS mutations, tend to co-exist with those in PIK3CA and mutated PI3K has been shown to interfere with the successful application of MEK inhibitors. When PLX4720 was used to treat colon tumours, results were not encouraging and herein we attempt to understand the cause of this recorded resistance and discover rational therapeutic combinations to resensitize oncogene driven tumours to apoptosis. Treatment of two genetically different BRAF(V600E) mutant colon cancer cell lines with PLX4720 conferred complete resistance to cell death. Even though p-MAPK/ ERK kinase (MEK) suppression was achieved, TRAIL, an apoptosis inducing agent, was used synergistically in order to achieve cell death by apoptosis in RKO(BRAFV600E/PIK3CAH1047) cells. In contrast, for the same level of apoptosis in HT29(BRAFV600E/PIK3CAP449T) cells, TRAIL was combined with 17-AAG, an Hsp90 inhibitor. For cells where PLX4720 was completely ineffective, 17-AAG was alternatively used to target mutant BRAF(V600E). TRAIL dependence on the constitutive activation of BRAF(V600E) is emphasised through the overexpression of BRAF(V600E) in the permissive genetic background of colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells. Pharmacological suppression of the PI3K pathway further enhances the synergistic effect between TRAIL and PLX4720 in RKO cells, indicating the presence of PIK3CA(MT) as the inhibitory factor. Another rational combination includes 17-AAG synergism with TRAIL in a BRAF(V600E) mutant dependent manner to commit cells to apoptosis, through DR5 and the amplification of the apoptotic pathway. We have successfully utilised combinations of two chemically unrelated BRAF(V600E) inhibitors in combination with TRAIL in a BRAF(V600E) mutated background and provided insight for new anti-cancer strategies where the activated PI3KCA mutation oncogene should be suppressed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Li WQ, Kawakami K, Ruszkiewicz A, Bennett G, Moore J, et al. BRAF mutations are associated with distinctive clinical, pathological and molecular features of colorectal cancer independently of microsatellite instability status. 2Mol Cancer. 2006;5 1476-4598-5-2 [pii];10.1186/1476-4598-5-2 [doi] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lowe SW, Cepero E, Evan G. Intrinsic tumour suppression. Nature. 2004;432:307–315. nature03098 [pii];10.1038/nature03098 [doi] - PubMed
-
- Ziegler U, Groscurth P. Morphological features of cell death. News Physiol Sci. 2004;19:124–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

