Aesthetic comparison of the ideal nasal radix height in Brazilians
- PMID: 21739008
- PMCID: PMC9443706
- DOI: 10.1590/s1808-86942011000300011
Aesthetic comparison of the ideal nasal radix height in Brazilians
Abstract
The harmony of the facial profile is widely influenced by the height and form of the nasal dorsum. A few millimeters can make the lateral view aesthetically more or less pleasing and adequate in a subject's face. Professionals working with facial aesthetics should focus not only on the surgical techniques for proposed outcomes, but also with the subtleties and subjectivity that characterize aesthetic concepts and judgment.
Material and methods: A prospective survey to evaluate the preferences of a group of healthcare professionals working with facial aesthetics, a group of fine artists, and lay people about the best nasal radix height; the survey involved comparing 3 different nasal radix heights using computer-altered photographs of women with measurements close to the Caucasian standard.
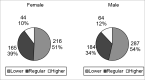
Results and conclusion: The lowest position of the nasal radix--close to the height of the pupil--was preferred (53%), followed by the middle position (superior crease of the eye). The highest position, resembling classic Greek statues, was considered the worst. The authors evaluated the effect of age, gender, and educational level on the choice of the best and worst female profiles.
Figures




References
-
- Farkas LG, Kolar JC, Munro IR. “Geography of the nose: a morphometric study.” Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1986;10(4):191–223. - PubMed
-
- Reis SAB, Abrão J, Capelozza Filho L, Claro CAA. Análise Facial Subje-tiva. Rev Dental Press Ortodon Ortop Facial. 2006;11(4):159–172.
-
- Eco U. A História da Beleza. Record; Rio de Janeiro: 2004.
-
- Toriumi DM. Structure approach in rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2005;10(1):1–22. - PubMed
-
- Akcam T, Friedman O, Cook TA. The effect on snoring of structural nasal valve dilatation with a butterfly graft. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130(11):1313–1318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

