Regional and mucosal memory T cells
- PMID: 21739671
- PMCID: PMC3224372
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2029
Regional and mucosal memory T cells
Abstract
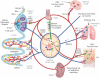
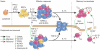
After infection, most antigen-specific memory T cells reside in nonlymphoid tissues. Tissue-specific programming during priming leads to directed migration of T cells to the appropriate tissue, which promotes the development of tissue-resident memory in organs such as intestinal mucosa and skin. Mechanisms that regulate the retention of tissue-resident memory T cells include transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-mediated induction of the E-cadherin receptor CD103 and downregulation of the chemokine receptor CCR7. These pathways enhance protection in internal organs, such as the nervous system, and in the barrier tissues--the mucosa and skin. Memory T cells that reside at these surfaces provide a first line of defense against subsequent infection, and defining the factors that regulate their development is critical to understanding organ-based immunity.
Figures

References
-
- Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Positive and negative selection of T cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003;21:139–176. - PubMed
-
- Sallusto F, Lenig D, Forster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature. 1999;401:708–712. - PubMed
-
- Reinhardt RL, Khoruts A, Merica R, Zell T, Jenkins MK. Visualizing the generation of memory CD4 T cells in the whole body. Nature. 2001;410:101–105. - PubMed
-
- Masopust D, Vezys V, Marzo AL, Lefrançois L. Preferential localization of effector memory cells in nonlymphoid tissue. Science. 2001;291:2413–2417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

