Proteasome inhibition in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myelogenous leukemia cell lines
- PMID: 21740082
- PMCID: PMC4557209
- DOI: 10.3109/07357907.2011.590567
Proteasome inhibition in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myelogenous leukemia cell lines
Abstract
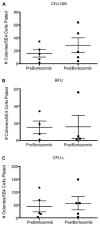
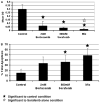
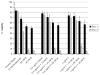
In this work, effects of bortezomib on apoptosis, clonal progenitor growth, cytokine production, and NF-κB expression in patients with MDS with cytopenias requiring transfusion support are examined. Bortezomib increased apoptosis in marrow mononuclear cells but had no effects on CFU-GM, BFU-E, or CFU-L content. No consistent effects on NF-κB activation in vivo were noted. To further define the role of bortezomib in AML and MDS, we examined it in combination with several targeted agents and chemotherapeutic agents in vitro. Combinations with arsenic trioxide, sorafenib, and cytarabine demonstrated synergistic in vitro effects in AML cell lines.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00262873.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

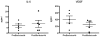









References
-
- Wu WK, Cho CH, Lee CW, Wu K, Fan D, Yu J, Sung JJ. Proteasome inhibition: a new therapeutic strategy to cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2010;293:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, Grimes B, Howard DS, Rizzieri DA, Luger SM, Jordan CT. Nuclear factor-kB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 2001;98:2301–2307. - PubMed
-
- Cilloni D, Martinelli G, Messa F, Baccarani M, Saglio G. Nuclear factor kB as a target for new drug development in myeloid malignancies. Haematologica. 2007;92:1224–1229. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Greten FR. NF-κB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev. 2005;5:749–759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
