Consequences of age-related cognitive declines
- PMID: 21740223
- PMCID: PMC3632788
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100328
Consequences of age-related cognitive declines
Abstract
Adult age differences in a variety of cognitive abilities are well documented, and many of those abilities have been found to be related to success in the workplace and in everyday life. However, increased age is seldom associated with lower levels of real-world functioning, and the reasons for this lab-life discrepancy are not well understood. This article briefly reviews research concerned with relations of age to cognition, relations of cognition to successful functioning outside the laboratory, and relations of age to measures of work performance and achievement. The final section discusses several possible explanations for why there are often little or no consequences of age-related cognitive declines in everyday functioning.
Figures


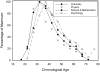
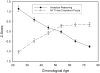
References
-
- Ackerman PL. Intelligence, attention and learning: maximal and typical performance. In: Detterman DK, editor. In Current Topics in Human Intelligence. Norwood, NJ: Ablex; 1994. pp. 1–27.
-
- Ackerman PL, Cianciolo AT. Ability and task constraint determinants of complex task performance. J Exp Psychol Appl. 2002;8:194–208. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, Driscoll J, Gabaix X, Laibson D. The age of reason: financial decisions over the lifecycle. Am Law Econ Assoc Annu Meet. 2008;97:1–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

