Molecular expression and enzymatic characterization of thioredoxin from the carcinogenic human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini
- PMID: 21740981
- PMCID: PMC3725289
- DOI: 10.1016/j.parint.2011.06.018
Molecular expression and enzymatic characterization of thioredoxin from the carcinogenic human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini
Abstract
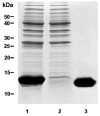
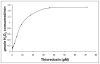
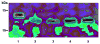
The human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, induces inflammation of the hepatobiliary system. Despite being constantly exposed to inimical oxygen radicals released from inflammatory cells, the parasite survives for years. Defense against oxidative damage can be mediated through glutathione and/or thioredoxin utilizing systems. Here, we report the molecular expression and biochemical characterization of a thioredoxin (Trx) from O. viverrini. O. viverrini Trx cDNA encoded a polypeptide of 105 amino acid residues, of molecular mass 11.63 kDa. The predicted protein has similarity to previously characterized thioredoxins with 26-51% identity. Recombinant O. viverrini Trx (Ov-Trx-1) was expressed as soluble protein in E. coli. The recombinant protein showed insulin reduction activity and supported the enzymatic function of O. viverrini thioredoxin peroxidase. Expression of Ov-Trx-1 at mRNA and protein levels was observed in all obtainable developmental stages of the liver fluke. Ov-Trx-1 was also detected in excretory-secretory products released by adult O. viverrini. Immunohistochemistry, Ov-Trx-1 was expressed in nearly all parasite tissue excepted ovary and mature sperms. Interestingly, Ov-Trx-1 was observed in the infected biliary epithelium but not in normal bile ducts. These results suggest that Ov-Trx-1 is essential for the parasite throughout the life cycle. In the host-parasite interaction aspect, Ov-Trx-1 may support thioredoxin peroxidase in protecting the parasite against damage induced by reactive oxygen species from inflammation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Characterization of the antioxidant enzyme, thioredoxin peroxidase, from the carcinogenic human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2008 Aug;160(2):116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.04.010. Epub 2008 May 2. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2008. PMID: 18538872 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin F cysteine protease of the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;3(3):e398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000398. Epub 2009 Mar 24. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 19308250 Free PMC article.
-
Asparaginyl endopeptidase from the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, and its potential for serodiagnosis.Int J Infect Dis. 2008 Nov;12(6):e49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.03.033. Epub 2008 Jul 10. Int J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18619888 Free PMC article.
-
Infection with the carcinogenic human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.Mol Biosyst. 2011 May;7(5):1367-75. doi: 10.1039/c0mb00295j. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Mol Biosyst. 2011. PMID: 21311794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opisthorchis viverrini: the carcinogenic human liver fluke.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Feb 7;14(5):666-74. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.666. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18205254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine Production in Cholangiocarcinoma Cells in Response to Clonorchis sinensis Excretory-Secretory Products and Their Putative Protein Components.Korean J Parasitol. 2019 Aug;57(4):379-387. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2019.57.4.379. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Korean J Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31533404 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Fluke-Associated Biliary Tract Cancer.Gut Liver. 2018 May 15;12(3):236-245. doi: 10.5009/gnl17102. Gut Liver. 2018. PMID: 28783896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis of cholangiocytes modulated by thioredoxin of carcinogenic liver fluke.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Aug;65:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.05.014. Epub 2015 May 23. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26007234 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and immunological characterization of thioredoxin transmembrane-related protein from Clonorchis sinensis.Parasitol Res. 2013 Apr;112(4):1729-36. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3331-5. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Parasitol Res. 2013. PMID: 23403994
-
Inflammatory pathways and cholangiocarcinoma risk mechanisms and prevention.Adv Cancer Res. 2022;156:39-73. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2022.02.001. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Adv Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35961707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jongsuksuntigul P, Imsomboon T. Opisthorchiasis control in Thailand. Acta Trop. 2003;88:229–32. - PubMed
-
- Sripa B, Kaewkes S. Localisation of parasite antigens and inflammatory responses in experimental opisthorchiasis. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30:735–40. - PubMed
-
- Kaewkes S. Taxonomy and biology of liver flukes. Acta Trop. 2003;88:177–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

