Selective killing of mixed lineage leukemia cells by a potent small-molecule DOT1L inhibitor
- PMID: 21741596
- PMCID: PMC4046888
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.009
Selective killing of mixed lineage leukemia cells by a potent small-molecule DOT1L inhibitor
Abstract
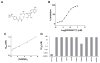
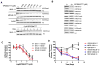
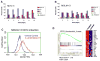
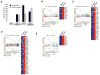
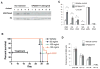
Mislocated enzymatic activity of DOT1L has been proposed as a driver of leukemogenesis in mixed lineage leukemia (MLL). The characterization of EPZ004777, a potent, selective inhibitor of DOT1L is reported. Treatment of MLL cells with the compound selectively inhibits H3K79 methylation and blocks expression of leukemogenic genes. Exposure of leukemic cells to EPZ004777 results in selective killing of those cells bearing the MLL gene translocation, with little effect on non-MLL-translocated cells. Finally, in vivo administration of EPZ004777 leads to extension of survival in a mouse MLL xenograft model. These results provide compelling support for DOT1L inhibition as a basis for targeted therapeutics against MLL.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong SA, Staunton JE, Silverman LB, Pieters R, den Boer ML, Minden MD, Sallan SE, Lander ES, Golub TR, Korsmeyer SJ. MLL translocations specify a distinct gene expression profile that distinguishes a unique leukemia. Nat Genet. 2002;30:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SA, Kung AL, Mabon ME, Silverman LB, Stam RW, Den Boer ML, Pieters R, Kersey JH, Sallan SE, Fletcher JA, et al. Inhibition of FLT3 in MLL. Validation of a therapeutic target identified by gene expression based classification. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:173–183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

