Plumbagin treatment leads to apoptosis in human K562 leukemia cells through increased ROS and elevated TRAIL receptor expression
- PMID: 21741707
- PMCID: PMC3163832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.06.018
Plumbagin treatment leads to apoptosis in human K562 leukemia cells through increased ROS and elevated TRAIL receptor expression
Abstract
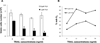
This study examined the ability of plumbagin to induce apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). Plumbagin exposure led to a significant reduction in cell viability and the induction of apoptosis. Mechanistically, plumbagin treatment led to elevated levels of ROS. Plumbagin-induced apoptosis was inhibited by N-acetyl L-cysteine (NAC) and PEG-catalase. Furthermore, plumbagin exposure led to elevated expression of DR4 and DR5 and increased killing through soluble TRAIL. The plumbagin-induced increase in DR4 and DR5 was inhibited by treatment with NAC. Together, this study suggests that plumbagin may be an effective treatment of CML through increased sensitivity to TRAIL-mediated killing.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report
Figures







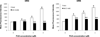
References
-
- Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 31;271(22):12687–12690. - PubMed
-
- Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995 Dec;3(6):673–682. - PubMed
-
- El-Deiry WS. Insights into cancer therapeutic design based on p53 and TRAIL receptor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2001 Nov;8(11):1066–1075. - PubMed
-
- Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T, Housman DE. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. - PubMed
-
- Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA, Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

