CD46 processing: a means of expression
- PMID: 21742405
- PMCID: PMC4363545
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imbio.2011.06.003
CD46 processing: a means of expression
Abstract
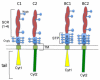
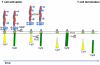
CD46 is a ubiquitously expressed type I transmembrane protein, first identified as a regulator of complement activation, and later as an entry receptor for a variety of pathogens. The last decade has also revealed the role of CD46 in regulating the adaptive immune response, acting as an additional costimulatory molecule for human T cells and inducing their differentiation into Tr1 cells, a subset of regulatory T cells. Interestingly, CD46 regulatory pathways are defective in T cells from patients with multiple sclerosis, asthma and rheumatoid arthritis, illustrating its importance in regulating T cell homeostasis. Indeed, CD46 expression at the cell surface is tightly regulated in many different cell types, highlighting its importance in several biological processes. Notably, CD46 is the target of enzymatic processing, being cleaved by metalloproteinases and by the presenilin/gamma secretase complex. This processing is required for its functions, at least in T cells. This review will summarize the latest updates on the regulation of CD46 expression and on its effects on T cell activation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T-cell regulation by CD46 and its relevance in multiple sclerosis.Immunology. 2008 Jun;124(2):149-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02821.x. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 18384356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamic processing of CD46 intracellular domains provides a molecular rheostat for T cell activation.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 19;6(1):e16287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016287. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21283821 Free PMC article.
-
CD46 plasticity and its inflammatory bias in multiple sclerosis.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2011 Feb;59(1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s00005-010-0109-7. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2011. PMID: 21267793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TCR-stimulated changes in cell surface CD46 expression generate type 1 regulatory T cells.Sci Signal. 2017 Oct 24;10(502):eaah6163. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aah6163. Sci Signal. 2017. PMID: 29066539
-
Monocyte:T-cell interaction regulates human T-cell activation through a CD28/CD46 crosstalk.Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;93(9):796-803. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.42. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25787182 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Calcitriol modulates the CD46 pathway in T cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048486. Epub 2012 Oct 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144765 Free PMC article.
-
LFA-1 in T cell priming, differentiation, and effector functions.Trends Immunol. 2021 Aug;42(8):706-722. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34266767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteolytic shedding of CD46 from human hepatocytes indicates liver stress.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 30;10(23):e40841. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40841. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39698100 Free PMC article.
-
Complement and the Regulation of T Cell Responses.Annu Rev Immunol. 2018 Apr 26;36:309-338. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053245. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29677470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HSP GRP94 interacts with macrophage intracellular complement C3 and impacts M2 profile during ER stress.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jan 22;12(1):114. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03288-x. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33483465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astier A, Trescol-Biemont MC, Azocar O, Lamouille B, Rabourdin-Combe C. Cutting edge: CD46, a new costimulatory molecule for T cells, that induces p120CBL and LAT phosphorylation. J Immunol. 2000;164:6091–6095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

