IRF4 deficiency abrogates lupus nephritis despite enhancing systemic cytokine production
- PMID: 21742731
- PMCID: PMC3148699
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010121260
IRF4 deficiency abrogates lupus nephritis despite enhancing systemic cytokine production
Abstract
The IFN-regulatory factors IRF1, IRF3, IRF5, and IRF7 modulate processes involved in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus and lupus nephritis, but the contribution of IRF4, which has multiple roles in innate and adaptive immunity, is unknown. To determine a putative pathogenic role of IRF4 in lupus, we crossed Irf4-deficient mice with autoimmune C57BL/6-(Fas)lpr mice. IRF4 deficiency associated with increased activation of antigen-presenting cells in C57BL/6-(Fas)lpr mice, resulting in a massive increase in plasma levels of TNF and IL-12p40, suggesting that IRF4 suppresses cytokine release in these mice. Nevertheless, IRF4 deficiency completely protected these mice from glomerulonephritis and lung disease. The mice were hypogammaglobulinemic and lacked antinuclear and anti-dsDNA autoantibodies, revealing the requirement of IRF4 for the maturation of plasma cells. As a consequence, Irf4-deficient C57BL/6-(Fas)lpr mice neither developed immune complex disease nor glomerular activation of complement. In addition, lack of IRF4 impaired the maturation of Th17 effector T cells and reduced plasma levels of IL-17 and IL-21, which are cytokines known to contribute to autoimmune tissue injury. In summary, IRF4 deficiency enhances systemic inflammation and the activation of antigen-presenting cells but also prevents the maturation of plasma cells and effector T cells. Because these adaptive immune effectors are essential for the evolution of lupus nephritis, we conclude that IRF4 promotes the development of lupus nephritis despite suppressing antigen-presenting cells.
Figures

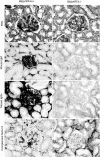




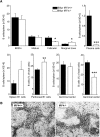
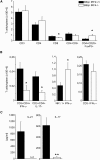
References
-
- Kotzin BL: Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell 85: 303–306, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Goodnow CC: Multistep pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Cell 130: 25–35, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Kanta H, Mohan C: Three checkpoints in lupus development: Central tolerance in adaptive immunity, peripheral amplification by innate immunity and end-organ inflammation. Genes Immun 10: 390–396, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH: Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 23: 307–336, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

