A comprehensive manually curated reaction map of RANKL/RANK-signaling pathway
- PMID: 21742767
- PMCID: PMC3170171
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bar021
A comprehensive manually curated reaction map of RANKL/RANK-signaling pathway
Abstract
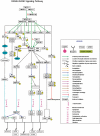
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) is a member of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily that plays a key role in the regulation of differentiation, activation and survival of osteoclasts and also in tumor cell migration and bone metastasis. Osteoclast activation induced by RANKL regulates hematopoietic stem cell mobilization as part of homeostasis and host defense mechanisms thereby linking regulation of hematopoiesis with bone remodeling. Binding of RANKL to its receptor, Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B (RANK) activates molecules such as NF-kappa B, mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and phosphatidyl 3-kinase (PI3K). Although the molecular and cellular roles of these molecules have been reported previously, a systematic cataloging of the molecular events induced by RANKL/RANK interaction has not been attempted. Here, we present a comprehensive reaction map of the RANKL/RANK-signaling pathway based on an extensive manual curation of the published literature. We hope that the curated RANKL/RANK-signaling pathway model would enable new biomedical discoveries, which can provide novel insights into disease processes and development of novel therapeutic interventions.
Figures

References
-
- Collin-Osdoby P, Rothe L, Anderson F, et al. Receptor activator of NF-kappa B and osteoprotegerin expression by human microvascular endothelial cells, regulation by inflammatory cytokines, and role in human osteoclastogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:20659–20672. - PubMed
-
- Lum L, Wong BR, Josien R, et al. Evidence for a role of a tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-converting enzyme-like protease in shedding of TRANCE, a TNF family member involved in osteoclastogenesis and dendritic cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:13613–13618. - PubMed
-
- Schlöndorff J, Lum L, Blobel CP, et al. Biochemical and pharmacological criteria define two shedding activities for TRANCE/OPGL that are distinct from the tumor necrosis factor alpha convertase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:14665–14674. - PubMed
-
- Chesneau V, Becherer JD, Zheng Y, et al. Catalytic properties of ADAM19. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:22331–22340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

