Early deaths during tuberculosis treatment are associated with depressed innate responses, bacterial infection, and tuberculosis progression
- PMID: 21742833
- PMCID: PMC3132140
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jir265
Early deaths during tuberculosis treatment are associated with depressed innate responses, bacterial infection, and tuberculosis progression
Abstract
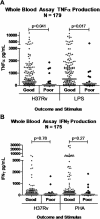
Up to 14% of Malawian adults die during the intensive phase of tuberculosis treatment. In a prospective cohort of 199 Malawian adults with microbiologically confirmed pulmonary tuberculosis, clinical and laboratory parameters were compared between those who died or deteriorated with those who had an uneventful recovery. Baseline tumor necrosis factor alpha responses to stimulation with heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis and lipopolysaccharide were reduced among the 22 patients with poor outcome (P = .017). Low body mass index (P = .002) and elevated respiratory rate (P = .01) at tuberculosis diagnosis independently predicted poor outcome. Validation of a clinical score identifying high-risk individuals is warranted, together with further investigation of immunological derangements.
Figures
References
-
- Harries AD, Hargreaves NJ, Gausi F, Kwanjana JH, Salaniponi FM. High early death rate in tuberculosis patients in Malawi. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001;5:1000–5. - PubMed
-
- Zachariah R, Fitzgerald M, Massaquoi M, et al. Does antiretroviral treatment reduce case fatality among HIV-positive patients with tuberculosis in Malawi? Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007;11:848–53. - PubMed
-
- Bekker LG, Maartens G, Steyn L, Kaplan G. Selective increase in plasma tumor necrosis factor-alpha and concomitant clinical deterioration after initiating therapy in patients with severe tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1998;178:580–4. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh SM, Hung CC, Chen MY, Sheng WH, Chang SC. Dynamics of plasma cytokine levels in patients with advanced HIV infection and active tuberculosis: implications for early recognition of patients with poor response to anti-tuberculosis treatment. AIDS. 1999;13:935–41. - PubMed
-
- Mootoo A, Stylianou E, Arias MA, Reljic R. TNF-alpha in tuberculosis: a cytokine with a split personality. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009;8:53–62. - PubMed

