L-arabitol is the actual inducer of xylanase expression in Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei)
- PMID: 21742908
- PMCID: PMC3165376
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.05427-11
L-arabitol is the actual inducer of xylanase expression in Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei)
Abstract
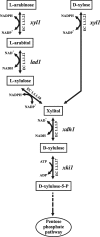
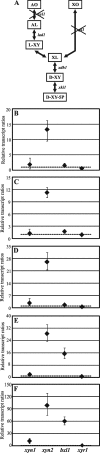
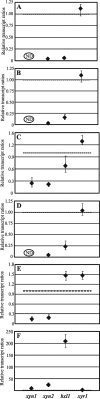
The saprophytic fungus Hypocrea jecorina (anamorph, Trichoderma reesei) is an important native producer of hydrolytic enzymes, including xylanases. Regarding principles of sustainability, cheap and renewable raw materials, such as d-xylose (the backbone monomer of xylan), have been receiving increasing attention from industries. Recently, it was demonstrated that small (0.5 to 1 mM) amounts of d-xylose induce the highest expression of xylanase in H. jecorina. However, it was also reported that active metabolism of d-xylose is necessary for induction. In this report, we demonstrate that xylitol, the next intermediate in the pentose pathway after d-xylose, does not trigger transcription of xylanase-encoding genes in H. jecorina QM9414. The highest level of transcription of xylanolytic enzyme-encoding genes occurred in an xdh1 (encoding a xylitol dehydrogenase) deletion strain cultured in the presence of 0.5 mM d-xylose, suggesting that a metabolite upstream of xylitol is the inducer. The expression levels of xylanases in an xdh1-lad1 double-deletion strain were lower than that of an xdh1 deletion strain. This observation suggested that l-xylulose is not an inducer and led to the hypothesis that l-arabitol is the actual inducer of xylanase expression. A direct comparison of transcript levels following the incubation of the H. jecorina parental strain with various metabolites of the pentose pathway confirmed this hypothesis. In addition, we demonstrate that xyr1, the activator gene, is not induced in the presence of pentose sugars and polyols, regardless of the concentration used; instead, we observed low constitutive expression of xyr1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
D-xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina: loss of the xylitol dehydrogenase step can be partially compensated for by lad1-encoded L-arabinitol-4-dehydrogenase.Eukaryot Cell. 2003 Oct;2(5):867-75. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.5.867-875.2003. Eukaryot Cell. 2003. PMID: 14555469 Free PMC article.
-
D-Xylose as a repressor or inducer of xylanase expression in Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei).Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Mar;76(6):1770-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02746-09. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20097821 Free PMC article.
-
Xyr1 (xylanase regulator 1) regulates both the hydrolytic enzyme system and D-xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Dec;5(12):2128-37. doi: 10.1128/EC.00211-06. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 17056741 Free PMC article.
-
[Transcriptional regulation of cellulases and hemicellulases gene in Hypocrea jecorina--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2010 Nov;50(11):1431-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 21268886 Review. Chinese.
-
Regulation of transcription of cellulases- and hemicellulases-encoding genes in Aspergillus niger and Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei).Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008 Feb;78(2):211-20. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1322-0. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18197406 Review.
Cited by
-
Light-inducible genetic engineering and control of non-homologous end-joining in industrial eukaryotic microorganisms: LML 3.0 and OFN 1.0.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 9;6:20761. doi: 10.1038/srep20761. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26857594 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Trichoderma reesei Mutant with Enhanced Xylanase Activity by Using Disparity Mutagenesis.J Appl Glycosci (1999). 2019 May 21;66(2):59-64. doi: 10.5458/jag.jag.JAG-2018_0004. eCollection 2019. J Appl Glycosci (1999). 2019. PMID: 34354521 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering transcriptional regulatory mechanisms associated with hemicellulose degradation in Neurospora crassa.Eukaryot Cell. 2012 Apr;11(4):482-93. doi: 10.1128/EC.05327-11. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Eukaryot Cell. 2012. PMID: 22345350 Free PMC article.
-
The Promoter Toolbox for Recombinant Gene Expression in Trichoderma reesei.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018 Oct 11;6:135. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00135. eCollection 2018. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30364340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal X-Intrinsic Protein Aquaporin from Trichoderma atroviride: Structural and Functional Considerations.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 23;11(2):338. doi: 10.3390/biom11020338. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33672420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aden A., Bozell J., Holladay J., White J., A. M. 2004. Top value added chemicals from biomass, vol. 1. U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge, TN
-
- de Vries R. P. 2003. Regulation of Aspergillus genes encoding plant cell wall polysaccharide-degrading enzymes: relevance for industrial production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 61:10–20 - PubMed
-
- Hrmova M., Biely P., Vrsanska M. 1986. Specificity of cellulase and ß-xylanase induction in Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Arch. Microbiol. 144:307–311
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

