Modulation of pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by inhibition of TAK1
- PMID: 21743023
- PMCID: PMC3149044
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djr243
Modulation of pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by inhibition of TAK1
Erratum in
-
Editor's Note: Modulation of Pancreatic Cancer Chemoresistance by Inhibition of TAK1.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2025 Feb 1;117(2):381. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djae312. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2025. PMID: 39657978 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: TGF-β-activated kinase-1 (TAK1), a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, functions in the activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1, which can suppress proapoptotic signaling pathways and thus promote resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. However, it is not known if inhibition of TAK1 is effective in reducing chemoresistance to therapeutic drugs against pancreatic cancer.
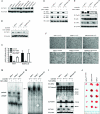
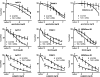
Methods: NF-κB activity was measured by luciferase reporter assay in human pancreatic cancer cell lines AsPc-1, PANC-1, and MDAPanc-28, in which TAK1 expression was silenced by small hairpin RNA. TAK1 kinase activity was targeted in AsPc-1, PANC-1, MDAPanc-28, and Colo357FG cells with exposure to increasing doses of a selective small-molecule inhibitor, LYTAK1, for 24 hours. To test the effect of LYTAK1 in combination with chemotherapeutic agents, AsPc-1, PANC-1, MDAPanc-28 cells, and control cells were treated with increasing doses of oxaliplatin, SN-38, or gemcitabine in combination with LYTAK1. In vivo activity of oral LYTAK1 was evaluated in an orthotopic nude mouse model (n = 40, 5 per group) with luciferase-expressing AsPc-1 pancreatic cancer cells. The results of in vitro proliferation were analyzed for statistical significance of differences by nonlinear regression analysis; differences in mouse survival were determined using a log-rank test. All statistical tests were two-sided.
Results: AsPc-1 and MDAPanc-28 TAK1 knockdown cells had a statistically significantly lower NF-κB activity than did their respective control cell lines (relative luciferase activity: AsPc-1, mean = 0.18, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.10 to 0.27; control, mean = 3.06, 95% CI = 2.31 to 3.80; MDAPanc-28, mean = 0.30, 95% CI = 0.13 to 0.46; control, mean = 4.53, 95% CI = 3.43 to 5.63; both P < .001). TAK1 inhibitor LYTAK1 had potent in vitro cytotoxic activity in AsPc-1, PANC-1, MDAPanc-28, and Colo357FG cells, with IC(50) between 5 and 40 nM. LYTAK1 also potentiated the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents oxaliplatin, SN-38, and gemcitabine in AsPc-1, PANC-1, and MDAPanc-28 cells compared with control cells (P < .001). In nude mice, oral administration of LYTAK1 plus gemcitabine statistically significantly reduced tumor burden (gemcitabine vs gemcitabine plus LYTAK1, P = .03) and prolonged survival duration (median survival: gemcitabine, 82 days vs gemcitabine plus LYTAK1, 122 days; hazard ratio = 0.334, 95% CI = 0.027 to 0.826, P = .029).
Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that genetic silencing or inhibition of TAK1 kinase activity in vivo is a potential therapeutic approach to reversal of the intrinsic chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer.
Figures

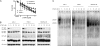



Comment in
-
Editor's Note: Modulation of Pancreatic Cancer Chemoresistance by Inhibition of TAK1.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2025 Feb 1;117(2):381. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djae312. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2025. PMID: 39657978 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300. - PubMed
-
- Melisi D, Chiao PJ. NF-kappa B as a target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007;11(2):133–144. - PubMed
-
- Verde P, Casalino L, Talotta F, Yaniv M, Weitzman JB. Deciphering AP-1 function in tumorigenesis: fra-ternizing on target promoters. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(21):2633–2639. - PubMed
-
- Rayet B, Gelinas C. Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene. 1999;18(49):6938–6947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

