Gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy
- PMID: 21743485
- PMCID: PMC4002534
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2011.82
Gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy
Abstract
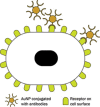
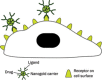
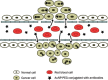
The rapid advancement of nanotechnology in recent years has fuelled a burgeoning interest in the field of nanoparticle research, in particular, its application in the medical arena. A constantly expanding knowledge based on a better understanding of the properties of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) coupled with relentless experimentation means that the frontiers of nanotechnology are constantly being challenged. At present, there seems to be heightened interest in the application of AuNPs to the management of cancer, encompassing diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of the disease. These efforts are undertaken in the hope of revolutionizing current methods of treatment and treatment strategies for a multifactorial disease such as cancer. This review will focus on the current applications of AuNPs in cancer management.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer [homepage on the Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization. Accessed Oct 21, 2010. Available from: : http://www.who.int/cancer/en/ .
-
- Wagstaff KM, Jans DA. Nuclear drug delivery to target tumour cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009;625:174–80. - PubMed
-
- Boisselier E, Astruc D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:1759–82. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Miyoshi H, Nakamura M. Nanomedicine for drug delivery and imaging: a promising avenue for cancer therapy and diagnosis using targeted functional nanoparticles. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:2527–37. - PubMed
-
- Lanone S, Boczkowski J. Biomedical applications and potential health risks of nanomaterials: molecular mechanisms. Curr Mol Med. 2006;6:651–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

