TRANSCRIPTIONAL AND PHOSPHO-PROTEOMIC SCREENS REVEAL STEM CELL ACTIVATION OF INSULIN-RESISTANCE AND TRANSFORMATION PATHWAYS FOLLOWING A SINGLE MINIMALLY TOXIC EPISODE OF ROS
- PMID: 21743783
- PMCID: PMC3131088
TRANSCRIPTIONAL AND PHOSPHO-PROTEOMIC SCREENS REVEAL STEM CELL ACTIVATION OF INSULIN-RESISTANCE AND TRANSFORMATION PATHWAYS FOLLOWING A SINGLE MINIMALLY TOXIC EPISODE OF ROS
Abstract
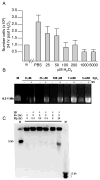
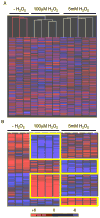
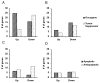
Elevated reactive oxidative species (ROS) are cytotoxic, and chronic elevated levels of ROS have been implicated in multiple diseases as well as cellular transformation and tumor progression. However, the potential for a transient and minimally toxic episode of ROS exposure, or a minimal threshold dose of ROS, to initiate disease or cellular transformation is unclear. We examined both transcriptional and phospho-proteomic responses of murine embryonic stem (ES) cells to a single brief exposure of minimally toxic hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)). The cellular response was distinct from those induced by either an acute exposure to H(2)O(2) or the topoisomerase II poison etoposide. Analysis of tumorigenesis-related transcripts revealed a significant up-regulation of oncogenes and down-regulation of tumor suppressors. Analysis of the phospho-proteomic response demonstrated insulin-signaling induction, including insulin receptor Y972 hypophosphorylation, similar to insulin-resistance mouse models and observed in diabetic patients. In addition, ES cells were more resistant to ROS than differentiated cells, and retained their transcriptional self-renewal signature, suggesting stem cells have a higher potential for ROS-mediated mutagenesis and proliferation in vivo. These results are a direct demonstration that even brief and non-toxic exposures to ROS may induce transduction of insulin resistance and transformation signaling in stem cells leading to diabetes and cancer.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
