Comparative analysis of placental vasculature and placental volume in normal and IUGR pregnancies with the use of three-dimensional Power Doppler
- PMID: 21744006
- PMCID: PMC3257431
- DOI: 10.1007/s00404-011-1968-9
Comparative analysis of placental vasculature and placental volume in normal and IUGR pregnancies with the use of three-dimensional Power Doppler
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the differences in placental vascular indices and placental volume between normal and IUGR pregnancies.
Methods: A prospective study was conducted on a group of 100 normal and 20 IUGR pregnancies between 22 and 42 weeks of gestation. For the purpose of evaluation of placental volume and placental vascular indices, we applied 3D Power Doppler and VOCAL technique. Only patients with entirely visualized placenta were included in the study.
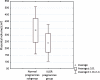
Results: A comparative analysis of vascularization index (VI), vascularization flow index (VFI), flow index (FI), and placental volume (PV) revealed statistically significant differences between normal and IUGR pregnancies. In normal pregnancies, the volume of the placenta was on average 92.42 cm(3) larger than in pregnancies complicated by IUGR. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to evaluate the clinical usefulness of placental vascular indices and placental volume for discriminating IUGR and normal pregnancies. It was concluded that the VI, VFI, PV, FI parameters are the best discriminants, with the cut-off values of 5.30, 2.30, 199, and 36.0, respectively.
Conclusions: The quantitative assessment of placental vasculature and placental volume by means of 3D Power Doppler and VOCAL technique is an adjunctive modality for differentiation between normal and IUGR pregnancies. Our findings further suggest that the vascularization index (VI) and vascularization flow index (VFI) are the best parameters with the most favorable discriminating potential for proper identification of IUGR pregnancies.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources