Rituximab in refractory Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease
- PMID: 21744181
- PMCID: PMC3223341
- DOI: 10.1007/s12348-011-0027-9
Rituximab in refractory Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease
Abstract
Introduction: Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) prognosis depends on early recognition and treatment; chronic disease may be developed when either delayed or inadequate treatment is performed, whereas other cases despite correct treatment are refractory to different drugs and also become chronic. We report a case of refractory VKH controlled with rituximab treatment.
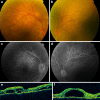
Case report: A 41-year-old female with painful visual loss and headache was examined. (VA 0.4 in RE and hand movements (HM) in LE). Retinal examination demonstrated multiple serous retinal detachments in both eyes. High-dose oral steroids were started, followed by progressive tapering of prednisone. New acute anterior and posterior relapses were achieved, and other immunommodulators were progressively added-new high-dose steroid treatment, adalimumab, cyclosporine, and methotrexate-but patient had new anterior and posterior recurrences associated with tinnitus and headache. Thus, an infusion of 1 g of rituximab was administered after 15 months follow-up; the VA was 0.2 in RE and counting fingers in LE. Three additional doses of 1 g each were administered 1, 6, and 16 months later. We have achieved a final VA after 34 months follow-up of 0.2 in RE and HM in LE, with definitive control of inflammation, without acute relapses since rituximab was administered.
Conclusion: After searching PubMed/Medline, this is the first report of VKH disease treated with rituximab. Additional studies are warranted to confirm the efficacy of this new approach for inflammatory control in refractory cases of VKH disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Corticotherapy vs. Corticotherapy Plus Immunosuppressive Therapy in Acute Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease.Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2018 May;93(5):225-230. doi: 10.1016/j.oftal.2017.09.010. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 29258782 English, Spanish.
-
Macular Hole Associated with Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease at the Acute Uveitic Stage.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2015 Sep 15;6(3):328-32. doi: 10.1159/000440679. eCollection 2015 Sep-Dec. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26483677 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Adalimumab for Chronic Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease Refractory to Conventional Corticosteroids and Immunosuppressive Therapy and Complicated by Central Serous Chorioretinopathy.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020 Apr 2;28(3):509-512. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2019.1603312. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 31268769
-
[Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2017 Jun;40(6):512-519. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Jun 1. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2017. PMID: 28579215 Review. French.
-
Diagnosis and classification of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Apr-May;13(4-5):550-5. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.023. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24440284 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms, Pathophysiology and Current Immunomodulatory/Immunosuppressive Therapy of Non-Infectious and/or Immune-Mediated Choroiditis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;15(4):398. doi: 10.3390/ph15040398. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome in a Ugandan: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges.Case Rep Med. 2019 Sep 16;2019:5192754. doi: 10.1155/2019/5192754. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Med. 2019. PMID: 31636673 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppressive therapy for Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease: a retrospective study and review of literature.J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2023 May 19;13(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12348-023-00333-6. J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2023. PMID: 37204477 Free PMC article.
-
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease: review of a rare autoimmune disease targeting antigens of melanocytes.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016 Mar 24;11:29. doi: 10.1186/s13023-016-0412-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016. PMID: 27008848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precise, simplified diagnostic criteria and optimised management of initial-onset Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease: an updated review.Eye (Lond). 2022 Jan;36(1):29-43. doi: 10.1038/s41433-021-01573-3. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Eye (Lond). 2022. PMID: 34145419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Díaz-Llopis M, Navea A, Peris C, Amselem L, Pinós J, Salom D, Hernández ML. Síndrome de Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada, actualización. Studium Ophthalologicum. 2004;22:157–166.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

