Insulin is differentially related to cognitive decline and atrophy in Alzheimer's disease and aging
- PMID: 21745566
- PMCID: PMC3264795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.06.011
Insulin is differentially related to cognitive decline and atrophy in Alzheimer's disease and aging
Abstract
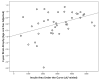
We assessed the relationship of insulin resistance with cognitive decline and brain atrophy over two years in early Alzheimer's disease (AD, n=48) and nondemented controls (n=61). Intravenous glucose tolerance tests were conducted at baseline to determine insulin area-under-the-curve (AUC). A standard battery of cognitive tasks and MRI were conducted at baseline and 2-year follow-up. In nondemented controls, higher baseline insulin AUC was associated with 2-year decline in global cognitive performance (beta=-0.36, p=0.005). In early AD, however, higher insulin AUC was associated with less decline in global cognitive performance (beta=0.26, p=0.06), slower global brain atrophy (beta=0.40, p=0.01) and less regional atrophy in the bilateral hippocampi and cingulate cortices. While insulin resistance is associated with cognitive decline in nondemented aging, higher peripheral insulin may have AD-specific benefits or insulin signaling may be affected by systemic physiologic changes associated with AD. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Imaging Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative disease.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any financial conflict of interests to report.
Figures


References
-
- Unger JW, Livingston JN, Moss AM. Insulin receptors in the central nervous system: Localization, signalling mechanisms and functional aspects. Progress in Neurobiology. 1991;36:343–362. - PubMed
-
- Adamo M, Raizada MK, LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors in the nervous system. Molecular Neurobiology. 1989;3:71–100. - PubMed
-
- van der Heide LP, Ramakers GMJ, Smidt MP. Insulin signaling in the central nervous system: Learning to survive. Progress in Neurobiology. 2006;79:205–221. - PubMed
-
- Zhao WQ, Townsend M. Insulin resistance and amyloidogenesis as common molecular foundation for type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792:482–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- KL2 RR033177/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031295/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG029615/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000001/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG029615/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03AG026374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23NS058252/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033673/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS058252/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG035042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- C76 HF00201/PHS HHS/United States
- M01 RR023940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG026374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034614/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

